Page 180 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 180
stratified cuboidal epithelium of the excretory ducts (6, 8), which continue
through the connective tissue and the stratified squamous epithelium of the skin
to the surface of the skin (see Fig. 4.11).
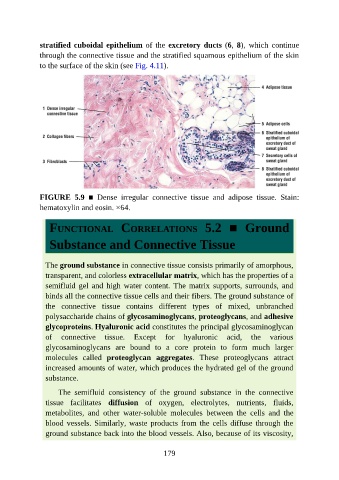
FIGURE 5.9 ■ Dense irregular connective tissue and adipose tissue. Stain:
hematoxylin and eosin. ×64.
FUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS 5.2 ■ Ground
Substance and Connective Tissue
The ground substance in connective tissue consists primarily of amorphous,
transparent, and colorless extracellular matrix, which has the properties of a
semifluid gel and high water content. The matrix supports, surrounds, and
binds all the connective tissue cells and their fibers. The ground substance of
the connective tissue contains different types of mixed, unbranched
polysaccharide chains of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, and adhesive
glycoproteins. Hyaluronic acid constitutes the principal glycosaminoglycan
of connective tissue. Except for hyaluronic acid, the various
glycosaminoglycans are bound to a core protein to form much larger
molecules called proteoglycan aggregates. These proteoglycans attract
increased amounts of water, which produces the hydrated gel of the ground
substance.
The semifluid consistency of the ground substance in the connective
tissue facilitates diffusion of oxygen, electrolytes, nutrients, fluids,
metabolites, and other water-soluble molecules between the cells and the
blood vessels. Similarly, waste products from the cells diffuse through the
ground substance back into the blood vessels. Also, because of its viscosity,
179