Page 680 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 680
FIGURE 17.18 | Section of Lung Alveoli Adjacent
to Bronchiole Wall
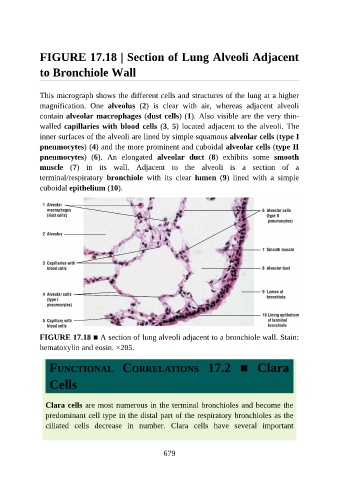
This micrograph shows the different cells and structures of the lung at a higher
magnification. One alveolus (2) is clear with air, whereas adjacent alveoli
contain alveolar macrophages (dust cells) (1). Also visible are the very thin-
walled capillaries with blood cells (3, 5) located adjacent to the alveoli. The
inner surfaces of the alveoli are lined by simple squamous alveolar cells (type I
pneumocytes) (4) and the more prominent and cuboidal alveolar cells (type II
pneumocytes) (6). An elongated alveolar duct (8) exhibits some smooth
muscle (7) in its wall. Adjacent to the alveoli is a section of a
terminal/respiratory bronchiole with its clear lumen (9) lined with a simple
cuboidal epithelium (10).
FIGURE 17.18 ■ A section of lung alveoli adjacent to a bronchiole wall. Stain:
hematoxylin and eosin. ×205.
FUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS 17.2 ■ Clara
Cells
Clara cells are most numerous in the terminal bronchioles and become the
predominant cell type in the distal part of the respiratory bronchioles as the
ciliated cells decrease in number. Clara cells have several important
679