Page 676 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 676
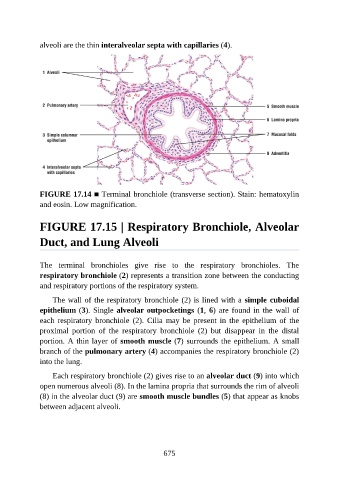
alveoli are the thin interalveolar septa with capillaries (4).
FIGURE 17.14 ■ Terminal bronchiole (transverse section). Stain: hematoxylin
and eosin. Low magnification.
FIGURE 17.15 | Respiratory Bronchiole, Alveolar
Duct, and Lung Alveoli
The terminal bronchioles give rise to the respiratory bronchioles. The
respiratory bronchiole (2) represents a transition zone between the conducting
and respiratory portions of the respiratory system.
The wall of the respiratory bronchiole (2) is lined with a simple cuboidal
epithelium (3). Single alveolar outpocketings (1, 6) are found in the wall of
each respiratory bronchiole (2). Cilia may be present in the epithelium of the
proximal portion of the respiratory bronchiole (2) but disappear in the distal
portion. A thin layer of smooth muscle (7) surrounds the epithelium. A small
branch of the pulmonary artery (4) accompanies the respiratory bronchiole (2)
into the lung.
Each respiratory bronchiole (2) gives rise to an alveolar duct (9) into which
open numerous alveoli (8). In the lamina propria that surrounds the rim of alveoli
(8) in the alveolar duct (9) are smooth muscle bundles (5) that appear as knobs
between adjacent alveoli.
675