Page 673 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 673
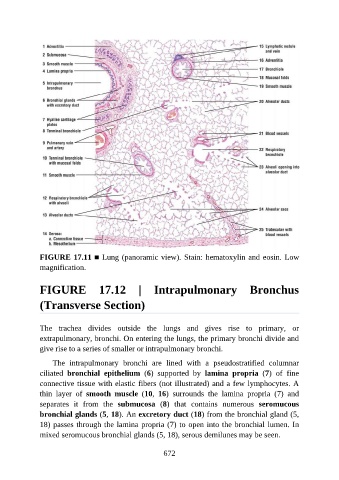
FIGURE 17.11 ■ Lung (panoramic view). Stain: hematoxylin and eosin. Low
magnification.
FIGURE 17.12 | Intrapulmonary Bronchus
(Transverse Section)
The trachea divides outside the lungs and gives rise to primary, or
extrapulmonary, bronchi. On entering the lungs, the primary bronchi divide and
give rise to a series of smaller or intrapulmonary bronchi.
The intrapulmonary bronchi are lined with a pseudostratified columnar
ciliated bronchial epithelium (6) supported by lamina propria (7) of fine
connective tissue with elastic fibers (not illustrated) and a few lymphocytes. A
thin layer of smooth muscle (10, 16) surrounds the lamina propria (7) and
separates it from the submucosa (8) that contains numerous seromucous
bronchial glands (5, 18). An excretory duct (18) from the bronchial gland (5,
18) passes through the lamina propria (7) to open into the bronchial lumen. In
mixed seromucous bronchial glands (5, 18), serous demilunes may be seen.
672