Page 678 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 678
FIGURE 17.16 ■ Lung: terminal bronchiole, respiratory bronchiole, alveolar
ducts, alveoli, and a blood vessel. Stain: hematoxylin and eosin. ×40.
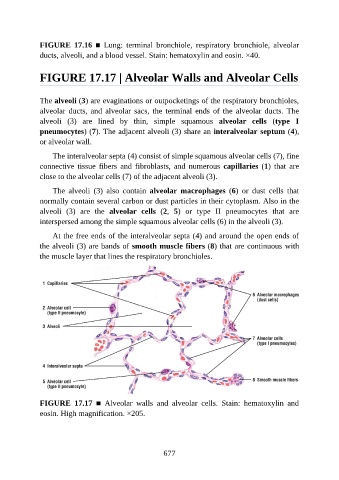
FIGURE 17.17 | Alveolar Walls and Alveolar Cells
The alveoli (3) are evaginations or outpocketings of the respiratory bronchioles,
alveolar ducts, and alveolar sacs, the terminal ends of the alveolar ducts. The
alveoli (3) are lined by thin, simple squamous alveolar cells (type I
pneumocytes) (7). The adjacent alveoli (3) share an interalveolar septum (4),
or alveolar wall.
The interalveolar septa (4) consist of simple squamous alveolar cells (7), fine
connective tissue fibers and fibroblasts, and numerous capillaries (1) that are
close to the alveolar cells (7) of the adjacent alveoli (3).
The alveoli (3) also contain alveolar macrophages (6) or dust cells that
normally contain several carbon or dust particles in their cytoplasm. Also in the
alveoli (3) are the alveolar cells (2, 5) or type II pneumocytes that are
interspersed among the simple squamous alveolar cells (6) in the alveoli (3).
At the free ends of the interalveolar septa (4) and around the open ends of
the alveoli (3) are bands of smooth muscle fibers (8) that are continuous with
the muscle layer that lines the respiratory bronchioles.
FIGURE 17.17 ■ Alveolar walls and alveolar cells. Stain: hematoxylin and
eosin. High magnification. ×205.
677