Page 20 - Wagp_InterfaceElectronic_Volume4_2015_US.pdf
P. 20
0 WAGO Overvoltage Protection
18
WAGO overvoltage protection Varistors have a very high resistance until their
for increased safety and longer threshold voltage is exceeded. Then they drop %
on-line operation to a low resistance and are capable of car- 100
90
rying high currents for a short period of time. __________> u u V
On-the-line overvoltages cause most ope- They have a fast response time, and have a 50
rating failures for measuring, control, data current carrying capacity dependent on the 30 û û V ˆ
and power lines. Failure of electronic and surface area of metal oxide material.
semiconductor components due to surges can MOVs can be sized to handle currents excee- 0
cause operating interruptions. The overvolt- ding of 100 kA. (_T _)
age (also called transients) can be generated Undersized varistors can age with con tinued _) T 1 = 1,2 ms(_
<__________ T 2 = 50 ms __________>
by switching electrical equipment on or off
or by lighting discharges. Devices designed
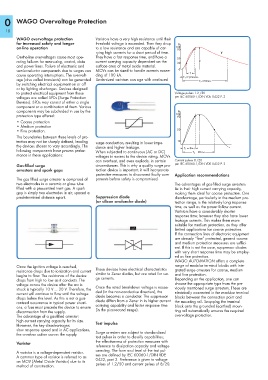
to protect electrical equipment from these Voltage pulses 1.2 /50
voltages are called SPDs (Surge Protection per IEC 60060-1 /DIN VDE 0432 P. 2
Devices). SPDs may consist of either a single
component or a combination of them. Various
components may be subdivided in use by the %
protection type offered: 100
90
• Coarse protection
• Medium protection
• Fine protection. 50
The boundaries between these levels of pro-
tection may not be sharply defined, leading surge conduction, resulting in lower impe- 10
the devices chosen to vary accordingly. The dance and higher leakage. T 1 = 8 ms
following components have proven perfor- When subjected to continuous (AC or DC)
mance in these applications: voltages in excess to the device rating, MOVs <_____ T 2 = 20 ms _____>
can overheat, and even explode, in certain Current pulses 8 /20
Gas-filled surge circumstances. This is why a quality surge pro- per IEC 60060-1 /DIN VDE 0432 P. 2
arresters and spark gaps tection device is important, it will incorporate
protective measures to disconnect faulty com- Application recommendations
The gas filled surge arrester is comprised of ponents before safety is compromised.
two electrodes in a ceramic or glass tube The advantages of gas-filled surge arresters
filled with a pressurized inert gas. A spark lie in their high current carrying capacity,
gap is simply two electrodes in air, spaced a making them ideal for coarse protection. One
predetermined distance apart. Suppression diode disadvantage, particularly in the medium pro-
(or silicon avalanche diode) tection range, is the relatively long response
time, as well as the power follow current.
Varistors have a considerably shorter
response time; however they also have lower
leakage currents. This makes them more
suitable for medium protection, as they offer
limited applications for coarse protection.
If the connection lines of electronic equipment
are already “fine” protected, general coarse
and medium protection measures are suffici-
ent. If this is not the case, suppressor diodes
with very short response time may be employ-
ed as fine protection.
WAGO AUTOMATION offers a complete
Once the ignition voltage is reached, range of modular terminal blocks with inte-
resistance drops due to ionization and current These devices have electrical characteristics grated surge arresters for coarse, medium
begins to flow. The resist ance of the device similar to Zener diodes, but are rated for sur- and fine protection.
drops from high to low as it conducts. The ge currents. Depending on the application, one can
voltage across the device after the arc is choose the appropriate type from the pre-
struck is typically 10 V ... 30 V. Therefore, the Once the rated breakdown voltage is excee- viously mentioned surge arresters. These are
current will continue to flow until the voltage ded (in the non-conductive direction), the electrically connected in the modular terminal
drops below this level. As this is not a gua- diode becomes a conductor. The suppressor blocks between the connection point and
ranteed occurrence in typical power situati- diode differs from a Zener in its higher current the mounting rail. Snapping the terminal
ons, a fuse must precede the device to ensure carrying capability and faster response time block onto the grounded (earthed) moun-
disconnection from the supply. (in the picosecond range). ting rail automatically ensures the required
The advantage of a gas-filled arrester: overvoltage protection.
high current carrying capacity for its size.
However, the key disadvantages: Test impulse
slow response speed and in AC applications,
the crowbar action across the supply. Surge arresters are subject to standardized
test pulses in order to classify capabilities;
the effectiveness of protection measures with
Varistor
reference to dissipation capacity and voltage
arresting. The form and level of the test pul-
A varistor is a voltage-dependent resis tor.
A common type of varistor is referred to as ses are defined by IEC 60060-1/DIN VDE
an MOV (Metal Oxide Varistor) due to its 0432, part 2. Preference is given to voltage
method of construction. pulses of 1.2/50 and current pulses of 8/20.