Page 70 - Carbon Frauds and Corruption
P. 70
Corruption of Bribery
Chapter 6 : Corruption in the “Carbon World”
Infrared Far 25(40) to 350 trapped by carbon dioxide
Microwave
Radio
Long Wave
Table 5: Wavelengths of Emissions from the Sun
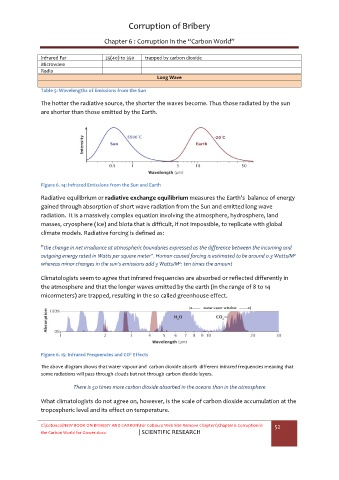
The hotter the radiative source, the shorter the waves become. Thus those radiated by the sun
are shorter than those emitted by the Earth.
Figure 6. 14: Infrared Emissions from the Sun and Earth
Radiative equilibrium or radiative exchange equilibrium measures the Earth’s balance of energy
gained through absorption of short wave radiation from the Sun and emitted long wave
radiation. It is a massively complex equation involving the atmosphere, hydrosphere, land
masses, cryosphere (Ice) and biota that is difficult, if not impossible, to replicate with global
climate models. Radiative forcing is defined as:
"the change in net irradiance at atmospheric boundaries expressed as the difference between the incoming and
outgoing energy rated in Watts per square meter". Human caused forcing is estimated to be around 0.3 Watts/M
2
whereas minor changes in the sun’s emissions add 3 Watts/M : ten times the amount
2
Climatologists seem to agree that infrared frequencies are absorbed or reflected differently in
the atmosphere and that the longer waves emitted by the earth (in the range of 8 to 14
micormeters) are trapped, resulting in the so called greenhouse effect.
2
Figure 6. 15: Infrared Frequencies and CO Effects
The above diagram shows that water vapour and carbon dioxide absorb different infrared frequencies meaning that
some radiations will pass through clouds but not through carbon dioxide layers.
There is 50 times more carbon dioxide absorbed in the oceans than in the atmosphere
What climatologists do not agree on, however, is the scale of carbon dioxide accumulation at the
tropospheric level and its effect on temperature.
C:\Cobasco\NEW BOOK ON BRIBERY AND CARBON\For Cobasco Web Site Remove Chapters\Chapter 6 Corruption in 52
the Carbon World for Gower.docx | SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH