Page 407 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 407
Printer: Yet to Come
October 9, 2014 8:1
JWST499-Cetinkunt
JWST499-c06
SENSORS 393 254mm×178mm
6.11 HUMIDITY SENSORS
Relative humidity is defined as the percentage ratio of the amount of water vapor in moist
air, versus the amount of water vapor in saturated air at a given temperature and pressure.
Relative humidity is strongly affected by temperature.
The main types of humidity sensors use the capacitance, resistive, and optical reflec-
tion principles in the transduction stage.
Capacitive humidity sensors use a polymer material which changes capacitance as
a function of humidity. The relationship is fairly linear. The sensor is designed as parallel
plates with porous electrodes on a substrate. The electrodes are coated with a dielectric
polymer material that absorbs water vapor from the environment with changes in humidity.
The resulting change in dielectric constant causes a variation in capacitance. The varia-
tion in capacitance is converted to voltage by an appropriate op-amp circuit to provide a
proportional voltage output.
Resistance based humidity sensors use materials on an electrode whose resistance
change as a function of humidity. In general, the resistance–humidity relationship is an
exponential relationship, and hence requires digital signal processing so that the voltage
output is proportional to the measured humidity. Capacitive humidity sensors are more
rugged and have less dependency on the temperature than the resistive humidity sensors.
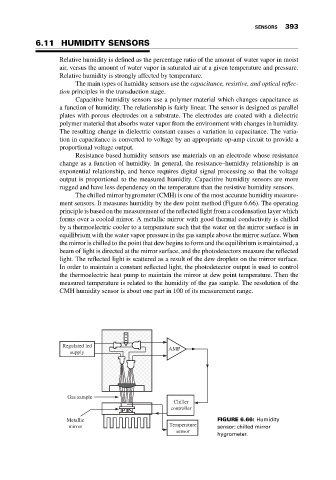
The chilled mirror hygrometer (CMH) is one of the most accurate humidity measure-
ment sensors. It measures humidity by the dew point method (Figure 6.66). The operating
principle is based on the measurement of the reflected light from a condensation layer which
forms over a cooled mirror. A metallic mirror with good thermal conductivity is chilled
by a thermoelectric cooler to a temperature such that the water on the mirror surface is in
equilibrium with the water vapor pressure in the gas sample above the mirror surface. When
the mirror is chilled to the point that dew begins to form and the equilibrium is maintained, a
beam of light is directed at the mirror surface, and the photodetectors measure the reflected
light. The reflected light is scattered as a result of the dew droplets on the mirror surface.
In order to maintain a constant reflected light, the photodetector output is used to control
the thermoelectric heat pump to maintain the mirror at dew point temperature. Then the
measured temperature is related to the humidity of the gas sample. The resolution of the
CMH humidity sensor is about one part in 100 of its measurement range.
Regulated led AMP
supply
Gas sample
Chiller
controller
Metallic FIGURE 6.66: Humidity
mirror Temperature sensor: chilled mirror
sensor
hygrometer.