Page 180 - Servo Motors and Industrial Control Theory -
P. 180
176 Appendix A
46. Repeat problem 45 for applications where the position of input shaft must be
controlled instead of angular velocity. In this case you should write all the equa-
tions in terms of angular position θ . i
47. In the transfer function obtained in problem 45, select some realistic engineer-
ing values for the parameters involved in the transfer function. Discuss on the
order of transfer function and sketch the frequency response and obtain the
frequency bandwidth of the system. Find the roots of characteristic equation
and obtain the corresponding damping ratio. Investigate the effect of viscous
damping coefficient C on the damping ratio of each of the complex roots.
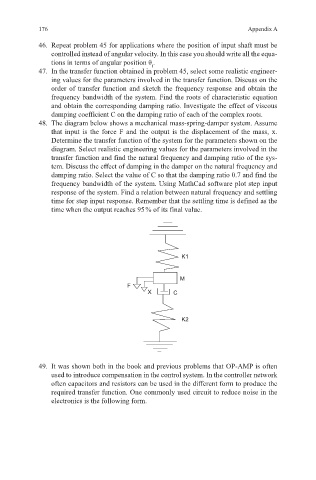
48. The diagram below shows a mechanical mass-spring-damper system. Assume
that input is the force F and the output is the displacement of the mass, x.
Determine the transfer function of the system for the parameters shown on the
diagram. Select realistic engineering values for the parameters involved in the
transfer function and find the natural frequency and damping ratio of the sys-
tem. Discuss the effect of damping in the damper on the natural frequency and
damping ratio. Select the value of C so that the damping ratio 0.7 and find the
frequency bandwidth of the system. Using MathCad software plot step input
response of the system. Find a relation between natural frequency and settling
time for step input response. Remember that the settling time is defined as the
time when the output reaches 95 % of its final value.
K1
M
F
X C
K2
49. It was shown both in the book and previous problems that OP-AMP is often
used to introduce compensation in the control system. In the controller network
often capacitors and resistors can be used in the different form to produce the
required transfer function. One commonly used circuit to reduce noise in the
electronics is the following form.