Page 29 - mathematics
P. 29
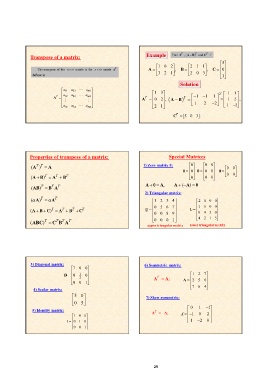
Transpose of a matrix: Example
A 1 0 2 , B 2 1 1 , 5
3 2 1 2 0 3 C 0
3
Solution
a11 a21 am1 1 3 T 1 1
a12 AT 0 2 , 1
AT a22 am2 1 A BT 1 1 1 1 2 ,
2 1 2 2
a1n
a2n amn 2
CT 5 0 3.
Properties of transpose of a matrix: Special Matrices
(AT )T A
1) Zero matrix 0: 0 0 0 0 0
(A B)T AT BT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
(AB)T BT AT 0 0
0 0
( A)T AT
A 0 A, A (A) 0
(A B C)T AT BT CT
2) Triangular matrix:
(ABC)T CT BT AT
1 2 3 4 -2 0 0 0
U 0 5 6 7 L 1 6 0 0
0 0 8 9 8 9 3 0
0 0 0 1 4 2 1 5
upper triangular matrix lower triangular matrix
3) Diagonal matrix: 6) Symmetric matrix:
7 0 0
D 0 0
1 AT A; 1 2 7
2 A 2 5 6
0 0 1
7 6 4
4) Scalar matrix:
5 0 7) Skew symmetric:
0 5
0 1 1
5) Identity matrix: AT A;
1 0 0 A 1 0 2
I 0 1 0 1 2 0
0 0 1
29