Page 508 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 508
498 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
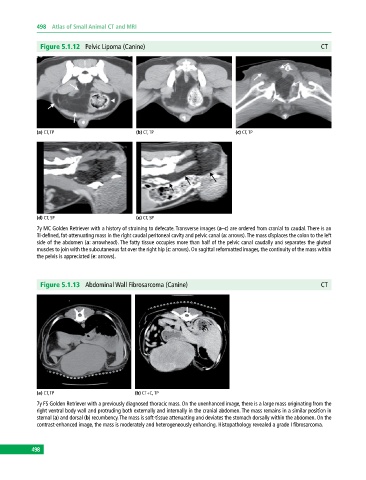
Figure 5.1.12 Pelvic Lipoma (Canine) CT
(a) CT, TP (b) CT, TP (c) CT, TP
(d) CT, SP (e) CT, SP
7y MC Golden Retriever with a history of straining to defecate. Transverse images (a–c) are ordered from cranial to caudal. There is an
ill‐defined, fat‐attenuating mass in the right caudal peritoneal cavity and pelvic canal (a: arrows). The mass displaces the colon to the left
side of the abdomen (a: arrowhead). The fatty tissue occupies more than half of the pelvic canal caudally and separates the gluteal
muscles to join with the subcutaneous fat over the right hip (c: arrows). On sagittal reformatted images, the continuity of the mass within
the pelvis is appreciated (e: arrows).
Figure 5.1.13 Abdominal Wall Fibrosarcoma (Canine) CT
(a) CT, TP (b) CT+C, TP
7y FS Golden Retriever with a previously diagnosed thoracic mass. On the unenhanced image, there is a large mass originating from the
right ventral body wall and protruding both externally and internally in the cranial abdomen. The mass remains in a similar position in
sternal (a) and dorsal (b) recumbency. The mass is soft‐tissue attenuating and deviates the stomach dorsally within the abdomen. On the
contrast‐enhanced image, the mass is moderately and heterogeneously enhancing. Histopathology revealed a grade I fibrosarcoma.
498