Page 552 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 552
542 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
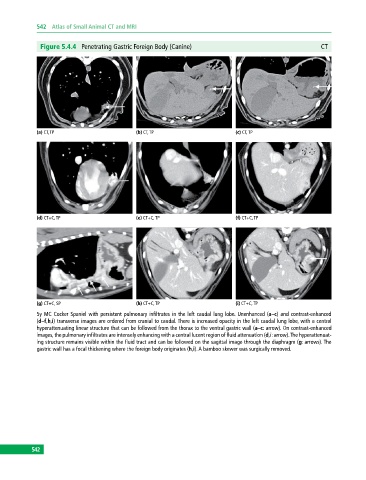
Figure 5.4.4 Penetrating Gastric Foreign Body (Canine) CT
(a) CT, TP (b) CT, TP (c) CT, TP
(d) CT+C, TP (e) CT+C, TP (f) CT+C, TP
(g) CT+C, SP (h) CT+C, TP (i) CT+C, TP
5y MC Cocker Spaniel with persistent pulmonary infiltrates in the left caudal lung lobe. Unenhanced (a–c) and contrast-enhanced
(d–f,h,i) transverse images are ordered from cranial to caudal. There is increased opacity in the left caudal lung lobe, with a central
hyperattenuating linear structure that can be followed from the thorax to the ventral gastric wall (a–c: arrow). On contrast‐enhanced
images, the pulmonary infiltrates are intensely enhancing with a central lucent region of fluid attenuation (d,i: arrow). The hyperattenuat-
ing structure remains visible within the fluid tract and can be followed on the sagittal image through the diaphragm (g: arrows). The
gastric wall has a focal thickening where the foreign body originates (h,i). A bamboo skewer was surgically removed.
542