Page 555 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 555
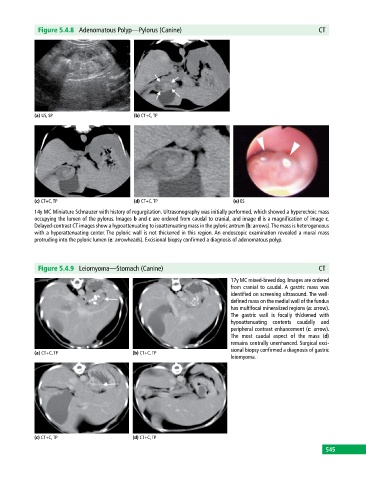
Figure 5.4.8 Adenomatous Polyp—Pylorus (Canine) CT
(a) US, SP (b) CT+C, TP
(c) CT+C, TP (d) CT+C, TP (e) ES
14y MC Miniature Schnauzer with history of regurgitation. Ultrasonography was initially performed, which showed a hyperechoic mass
occupying the lumen of the pylorus. Images b and c are ordered from caudal to cranial, and image d is a magnification of image c.
Delayed‐contrast CT images show a hypoattenuating to isoattenuating mass in the pyloric antrum (b: arrows). The mass is heterogeneous
with a hyperattenuating center. The pyloric wall is not thickened in this region. An endoscopic examination revealed a mural mass
protruding into the pyloric lumen (e: arrowheads). Excisional biopsy confirmed a diagnosis of adenomatous polyp.
Figure 5.4.9 Leiomyoma—Stomach (Canine) CT
17y MC mixed‐breed dog. Images are ordered
from cranial to caudal. A gastric mass was
identified on screening ultrasound. The well‐
defined mass on the medial wall of the fundus
has multifocal mineralized regions (a: arrow).
The gastric wall is focally thickened with
hypoattenuating contents caudally and
peripheral contrast enhancement (c: arrow).
The most caudal aspect of the mass (d)
remains centrally unenhanced. Surgical exci-
sional biopsy confirmed a diagnosis of gastric
(a) CT+C, TP (b) CT+C, TP
leiomyoma.
(c) CT+C, TP (d) CT+C, TP
545