Page 559 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 559
Gastrointestinal Tract 549
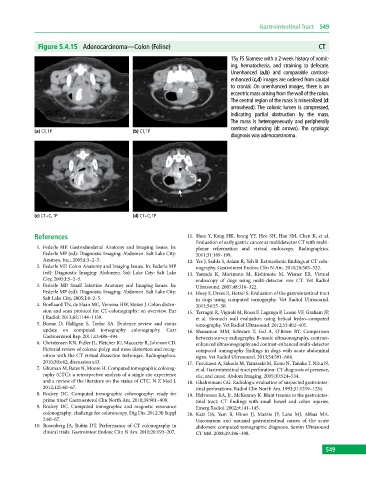
Figure 5.4.15 Adenocarcinoma—Colon (Feline) CT
15y FS Siamese with a 2‐week history of vomit-
ing, hematochezia, and straining to defecate.
Unenhanced (a,b) and comparable contrast-
enhanced (c,d) images are ordered from caudal
to cranial. On unenhanced images, there is an
eccentric mass arising from the wall of the colon.
The central region of the mass is mineralized (d:
arrowhead). The colonic lumen is compressed,
indicating partial obstruction by the mass.
The mass is heterogeneously and peripherally
contrast enhancing (d: arrows). The cytologic
(a) CT, TP (b) CT, TP
diagnosis was adenocarcinoma.
(c) CT+C, TP (d) CT+C, TP
References 11. Shen Y, Kang HK, Jeong YY, Heo SH, Han SM, Chen K, et al.
Evaluation of early gastric cancer at multidetector CT with multi
1. Federle MP. Gastroduodenal Anatomy and Imaging Issues. In: planar reformation and virtual endoscopy. Radiographics.
Federle MP (ed): Diagnostic Imaging: Abdomen. Salt Lake City: 2011;31:189–199.
Amirsys, Inc., 2005;I:3–2–5. 12. Yee J, Sadda S, Aslam R, Yeh B. Extracolonic findings at CT colo
2. Federle MP. Colon Anatomy and Imaging Issues. In: Federle MP nography. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2010;20:305–322.
(ed): Diagnostic Imaging: Abdomen. Salt Lake City: Salt Lake 13. Yamada K, Morimoto M, Kishimoto M, Wisner ER. Virtual
City, 2005;I:5–2–5. endoscopy of dogs using multi‐detector row CT. Vet Radiol
3. Federle MP. Small Intestine Anatomy and Imaging Issues. In: Ultrasound. 2007;48:318–322.
Federle MP (ed): Diagnostic Imaging: Abdomen. Salt Lake City: 14. Hoey S, Drees R, Hetzel S. Evaluation of the gastrointestinal tract
Salt Lake City, 2005;I:4–2–5. in dogs using computed tomography. Vet Radiol Ultrasound.
4. Boellaard TN, de Haan MC, Venema HW, Stoker J. Colon disten 2013;54:25–30.
sion and scan protocol for CT‐colonography: an overview. Eur 15. Terragni R, Vignoli M, Rossi F, Laganga P, Leone VF, Graham JP,
J Radiol. 2013;82:1144–1158. et al. Stomach wall evaluation using helical hydro–computed
5. Boone D, Halligan S, Taylor SA. Evidence review and status tomography. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2012;53:402–405.
update on computed tomography colonography. Curr 16. Shanaman MM, Schwarz T, Gal A, O’Brien RT. Comparison
Gastroenterol Rep. 2011;13:486–494. between survey radiography, B‐mode ultrasonography, contrast‐
6. Christensen KN, Fidler JL, Fletcher JG, Maccarty R, Johnson CD. enhanced ultrasonography and contrast‐enhanced multi‐ detector
Pictorial review of colonic polyp and mass distortion and recog computed tomography findings in dogs with acute abdominal
nition with the CT virtual dissection technique. Radiographics. signs. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2013;54:591–604.
2010;30:e42; discussion e43. 17. Furukawa A, Sakoda M, Yamasaki M, Kono N, Tanaka T, Nitta N,
7. Ghuman M, Bates N, Moore H. Computed tomographic colonog et al. Gastrointestinal tract perforation: CT diagnosis of presence,
raphy (CTC): a retrospective analysis of a single site experience site, and cause. Abdom Imaging. 2005;30:524–534.
and a review of the literature on the status of CTC. N Z Med J. 18. Ghahremani GG. Radiologic evaluation of suspected gastrointes
2012;125:60–67. tinal perforations. Radiol Clin North Am. 1993;31:1219–1234.
8. Rockey DC. Computed tomographic colonography: ready for 19. Halvorsen RA, Jr., McKenney K. Blunt trauma to the gastrointes
prime time? Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2010;39:901–909. tinal tract: CT findings with small bowel and colon injuries.
9. Rockey DC. Computed tomographic and magnetic resonance Emerg Radiol. 2002;9:141–145.
colonography: challenge for colonoscopy. Dig Dis. 2012;30 Suppl 20. Katz DS, Yam B, Hines JJ, Mazzie JP, Lane MJ, Abbas MA.
2:60–67. Uncommon and unusual gastrointestinal causes of the acute
10. Rosenberg JA, Rubin DT. Performance of CT colonography in abdomen: computed tomographic diagnosis. Semin Ultrasound
clinical trials. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2010;20:193–207. CT MR. 2008;29:386–398.
549