Page 562 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 562
552 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
attenuating with thin to irregularly thickened borders. were best seen during the arterial phase, where strong
Inflammatory lesions are often peripherally contrast contrast enhancement was present (Figure 5.5.9). Few
9
enhancing. Regions of tissue necrosis may fail to cases have been reported, and alternate enhancement
enhance on contrast images. Inflammatory pancreatic patterns are possible (Figure 5.5.10). An increase in the
cysts may occur, appearing as multilocular, fluid‐filled number of tortuous vessels may be visible in the arterial
masses on CT images. 8 phase, with heterogeneous contrast enhancement in
the delayed phase. If the mass is large enough, the con
tour of the pancreatic lobe may be focally altered.
Neoplasia
Angiography is also advantageous in evaluating for local
Insulinomas of the pancreas cause hypoglycemia and vascular invasion.
can lead to seizures. These tumors are often of small size Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas occurs in dogs
and are difficult to localize both on ultrasound and on and cats. Irregular masses that deform the pancreatic
CT images. The addition of dual‐phase CT angiography margins may be present with heterogeneous contrast
in evaluating for insulinoma maximizes the chance that enhancement and regions of necrosis (Figure 5.5.11).
attenuation differences will be visible for a small mass. A Local lymph nodes and liver should be evaluated for
report of three dogs with insulinoma found that masses evidence of metastatic disease.
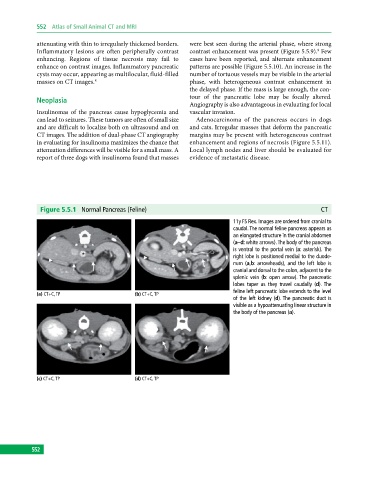
Figure 5.5.1 Normal Pancreas (Feline) CT
11y FS Rex. Images are ordered from cranial to
caudal. The normal feline pancreas appears as
an elongated structure in the cranial abdomen
(a–d: white arrows). The body of the pancreas
is ventral to the portal vein (a: asterisk). The
right lobe is positioned medial to the duode-
num (a,b: arrowheads), and the left lobe is
cranial and dorsal to the colon, adjacent to the
splenic vein (b: open arrow). The pancreatic
lobes taper as they travel caudally (d). The
feline left pancreatic lobe extends to the level
(a) CT+C, TP (b) CT+C, TP
of the left kidney (d). The pancreatic duct is
visible as a hypoattenuating linear structure in
the body of the pancreas (a).
(c) CT+C, TP (d) CT+C, TP
552