Page 564 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 564
554 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
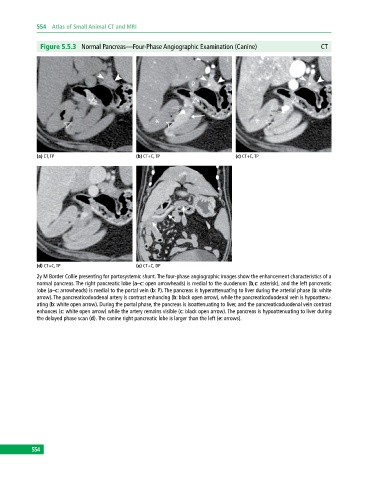
Figure 5.5.3 Normal Pancreas—Four‐Phase Angiographic Examination (Canine) CT
(a) CT, TP (b) CT+C, TP (c) CT+C, TP
(d) CT+C, TP (e) CT+C, DP
2y M Border Collie presenting for portosystemic shunt. The four‐phase angiographic images show the enhancement characteristics of a
normal pancreas. The right pancreatic lobe (a–c: open arrowheads) is medial to the duodenum (b,c: asterisk), and the left pancreatic
lobe (a–c: arrowheads) is medial to the portal vein (b: P). The pancreas is hyperattenuating to liver during the arterial phase (b: white
arrow). The pancreaticoduodenal artery is contrast enhancing (b: black open arrow), while the pancreaticoduodenal vein is hypoattenu-
ating (b: white open arrow). During the portal phase, the pancreas is isoattenuating to liver, and the pancreaticoduodenal vein contrast
enhances (c: white open arrow) while the artery remains visible (c: black open arrow). The pancreas is hypoattenuating to liver during
the delayed phase scan (d). The canine right pancreatic lobe is larger than the left (e: arrows).
554