Page 588 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 588
578 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
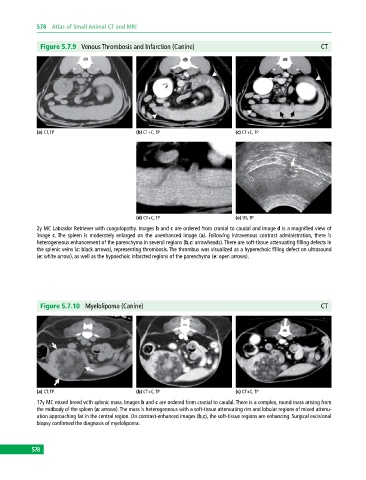
Figure 5.7.9 Venous Thrombosis and Infarction (Canine) CT
(a) CT, TP (b) CT+C, TP (c) CT+C, TP
(d) CT+C, TP (e) US, TP
2y MC Labrador Retriever with coagulopathy. Images b and c are ordered from cranial to caudal and image d is a magnified view of
image c. The spleen is moderately enlarged on the unenhanced image (a). Following intravenous contrast administration, there is
heterogeneous enhancement of the parenchyma in several regions (b,c: arrowheads). There are soft‐tissue attenuating filling defects in
the splenic veins (c: black arrows), representing thrombosis. The thrombus was visualized as a hyperechoic filling defect on ultrasound
(e: white arrow), as well as the hypoechoic infarcted regions of the parenchyma (e: open arrows).
Figure 5.7.10 Myelolipoma (Canine) CT
(a) CT, TP (b) CT+C, TP (c) CT+C, TP
17y MC mixed breed with splenic mass. Images b and c are ordered from cranial to caudal. There is a complex, round mass arising from
the midbody of the spleen (a: arrows). The mass is heterogeneous with a soft‐tissue attenuating rim and lobular regions of mixed attenu
ation approaching fat in the central region. On contrast‐enhanced images (b,c), the soft‐tissue regions are enhancing. Surgical excisional
biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of myelolipoma.
578