Page 599 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 599
Urinary Tract 589
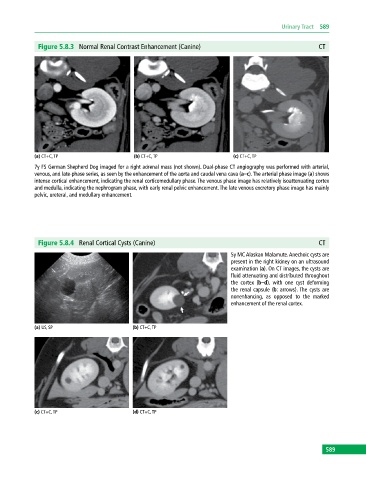
Figure 5.8.3 Normal Renal Contrast Enhancement (Canine) CT
(a) CT+C, TP (b) CT+C, TP (c) CT+C, TP
7y FS German Shepherd Dog imaged for a right adrenal mass (not shown). Dual‐phase CT angiography was performed with arterial,
venous, and late‐phase series, as seen by the enhancement of the aorta and caudal vena cava (a–c). The arterial phase image (a) shows
intense cortical enhancement, indicating the renal corticomedullary phase. The venous phase image has relatively isoattenuating cortex
and medulla, indicating the nephrogram phase, with early renal pelvic enhancement. The late venous excretory phase image has mainly
pelvic, ureteral, and medullary enhancement.
Figure 5.8.4 Renal Cortical Cysts (Canine) CT
5y MC Alaskan Malamute. Anechoic cysts are
present in the right kidney on an ultrasound
examination (a). On CT images, the cysts are
fluid attenuating and distributed throughout
the cortex (b–d), with one cyst deforming
the renal capsule (b: arrows). The cysts are
nonenhancing, as opposed to the marked
enhancement of the renal cortex.
(a) US, SP (b) CT+C, TP
(c) CT+C, TP (d) CT+C, TP
589