Page 604 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 604
594 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
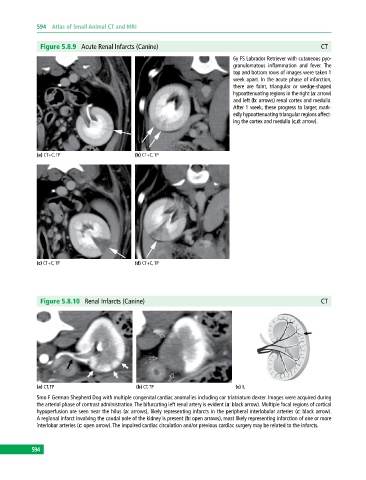
Figure 5.8.9 Acute Renal Infarcts (Canine) CT
6y FS Labrador Retriever with cutaneous pyo-
granulomatous inflammation and fever. The
top and bottom rows of images were taken 1
week apart. In the acute phase of infarction,
there are faint, triangular or wedge‐shaped
hypoattenuating regions in the right (a: arrow)
and left (b: arrows) renal cortex and medulla.
After 1 week, these progress to larger, mark-
edly hypoattenuating triangular regions affect-
ing the cortex and medulla (c,d: arrow).
(a) CT+C, TP (b) CT+C, TP
(c) CT+C, TP (d) CT+C, TP
Figure 5.8.10 Renal Infarcts (Canine) CT
(a) CT, TP (b) CT, TP (c) IL
5mo F German Shepherd Dog with multiple congenital cardiac anomalies including cor triatriatum dexter. Images were acquired during
the arterial phase of contrast administration. The bifurcating left renal artery is evident (a: black arrow). Multiple focal regions of cortical
hypoperfusion are seen near the hilus (a: arrows), likely representing infarcts in the peripheral interlobular arteries (c: black arrow).
A regional infarct involving the caudal pole of the kidney is present (b: open arrows), most likely representing infarction of one or more
interlobar arteries (c: open arrow). The impaired cardiac circulation and/or previous cardiac surgery may be related to the infarcts.
594