Page 605 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 605
Urinary Tract 595
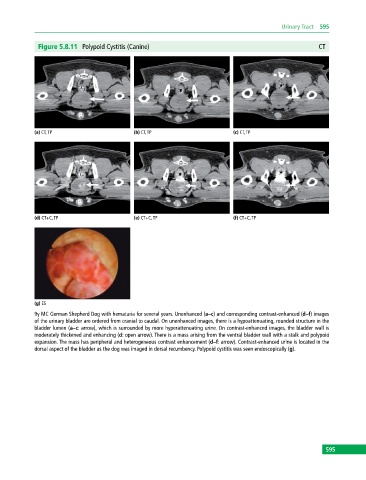
Figure 5.8.11 Polypoid Cystitis (Canine) CT
(a) CT, TP (b) CT, TP (c) CT, TP
(d) CT+C, TP (e) CT+C, TP (f) CT+C, TP
(g) ES
9y MC German Shepherd Dog with hematuria for several years. Unenhanced (a–c) and corresponding contrast-enhanced (d–f) images
of the urinary bladder are ordered from cranial to caudal. On unenhanced images, there is a hypoattenuating, rounded structure in the
bladder lumen (a–c: arrow), which is surrounded by more hyperattenuating urine. On contrast‐enhanced images, the bladder wall is
moderately thickened and enhancing (d: open arrow). There is a mass arising from the ventral bladder wall with a stalk and polypoid
expansion. The mass has peripheral and heterogeneous contrast enhancement (d–f: arrow). Contrast‐enhanced urine is located in the
dorsal aspect of the bladder as the dog was imaged in dorsal recumbency. Polypoid cystitis was seen endoscopically (g).
595