Page 610 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 610
600 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
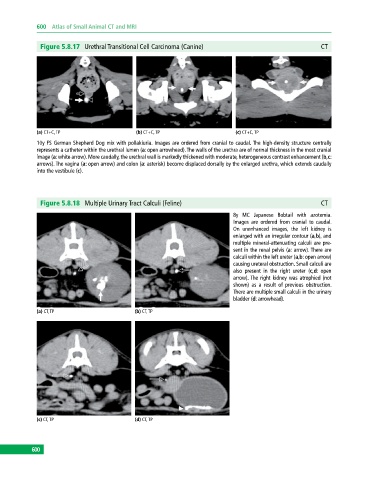
Figure 5.8.17 Urethral Transitional Cell Carcinoma (Canine) CT
(a) CT+C, TP (b) CT+C, TP (c) CT+C, TP
10y FS German Shepherd Dog mix with pollakiuria. Images are ordered from cranial to caudal. The high‐density structure centrally
represents a catheter within the urethral lumen (a: open arrowhead). The walls of the urethra are of normal thickness in the most cranial
image (a: white arrow). More caudally, the urethral wall is markedly thickened with moderate, heterogeneous contrast enhancement (b,c:
arrows). The vagina (a: open arrow) and colon (a: asterisk) become displaced dorsally by the enlarged urethra, which extends caudally
into the vestibule (c).
Figure 5.8.18 Multiple Urinary Tract Calculi (Feline) CT
8y MC Japanese Bobtail with azotemia.
Images are ordered from cranial to caudal.
On unenhanced images, the left kidney is
enlarged with an irregular contour (a,b), and
multiple mineral‐attenuating calculi are pre-
sent in the renal pelvis (a: arrow). There are
calculi within the left ureter (a,b: open arrow)
causing ureteral obstruction. Small calculi are
also present in the right ureter (c,d: open
arrow). The right kidney was atrophied (not
shown) as a result of previous obstruction.
There are multiple small calculi in the urinary
bladder (d: arrowhead).
(a) CT, TP (b) CT, TP
(c) CT, TP (d) CT, TP
600