Page 611 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 611
Urinary Tract 601
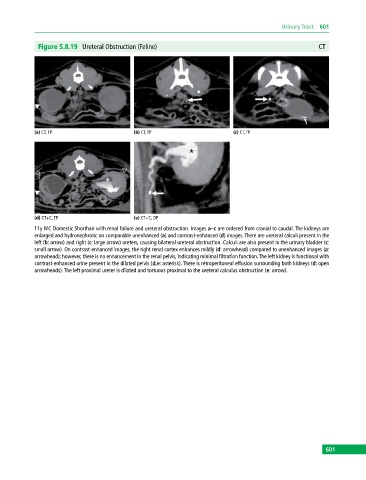
Figure 5.8.19 Ureteral Obstruction (Feline) CT
(a) CT, TP (b) CT, TP (c) CT, TP
(d) CT+C, TP (e) CT+C, DP
11y MC Domestic Shorthair with renal failure and ureteral obstruction. Images a–c are ordered from cranial to caudal. The kidneys are
enlarged and hydronephrotic on comparable unenhanced (a) and contrast‐enhanced (d) images. There are ureteral calculi present in the
left (b: arrow) and right (c: large arrow) ureters, causing bilateral ureteral obstruction. Calculi are also present in the urinary bladder (c:
small arrow). On contrast‐enhanced images, the right renal cortex enhances mildly (d: arrowhead) compared to unenhanced images (a:
arrowhead); however, there is no enhancement in the renal pelvis, indicating minimal filtration function. The left kidney is functional with
contrast‐enhanced urine present in the dilated pelvis (d,e: asterisk). There is retroperitoneal effusion surrounding both kidneys (d: open
arrowheads). The left proximal ureter is dilated and tortuous proximal to the ureteral calculus obstruction (e: arrow).
601