Page 670 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 670
660 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
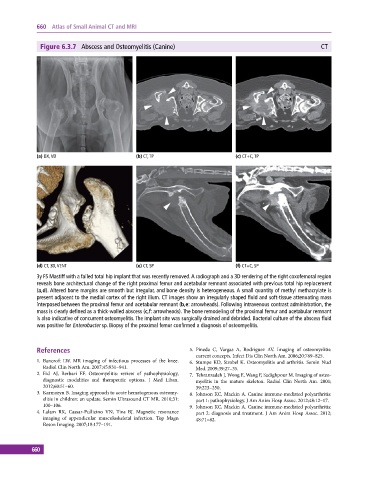
Figure 6.3.7 Abscess and Osteomyelitis (Canine) CT
(a) DX, VD (b) CT, TP (c) CT+C, TP
(d) CT, 3D, VENT (e) CT, SP (f) CT+C, SP
3y FS Mastiff with a failed total hip implant that was recently removed. A radiograph and a 3D rendering of the right coxofemoral region
reveals bone architectural change of the right proximal femur and acetabular remnant associated with previous total hip replacement
(a,d). Altered bone margins are smooth but irregular, and bone density is heterogeneous. A small quantity of methyl methacrylate is
present adjacent to the medial cortex of the right ilium. CT images show an irregularly shaped fluid and soft‐tissue attenuating mass
interposed between the proximal femur and acetabular remnant (b,e: arrowheads). Following intravenous contrast administration, the
mass is clearly defined as a thick‐walled abscess (c,f: arrowheads). The bone remodeling of the proximal femur and acetabular remnant
is also indicative of concurrent osteomyelitis. The implant site was surgically drained and debrided. Bacterial culture of the abscess fluid
was positive for Enterobacter sp. Biopsy of the proximal femur confirmed a diagnosis of osteomyelitis.
References 5. Pineda C, Vargas A, Rodriguez AV. Imaging of osteomyelitis:
current concepts. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2006;20:789–825.
1. Bancroft LW. MR imaging of infectious processes of the knee. 6. Stumpe KD, Strobel K. Osteomyelitis and arthritis. Semin Nucl
Radiol Clin North Am. 2007;45:931–941. Med. 2009;39:27–35.
2. Eid AJ, Berbari EF. Osteomyelitis: review of pathophysiology, 7. Tehranzadeh J, Wong E, Wang F, Sadighpour M. Imaging of osteo-
diagnostic modalities and therapeutic options. J Med Liban. myelitis in the mature skeleton. Radiol Clin North Am. 2001;
2012;60:51–60. 39:223–250.
3. Karmazyn B. Imaging approach to acute hematogenous osteomy- 8. Johnson KC, Mackin A. Canine immune‐mediated polyarthritis:
elitis in children: an update. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2010;31: part 1: pathophysiology. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 2012;48:12–17.
100–106. 9. Johnson KC, Mackin A. Canine immune‐mediated polyarthritis:
4. Lalam RK, Cassar‐Pullicino VN, Tins BJ. Magnetic resonance part 2: diagnosis and treatment. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 2012;
imaging of appendicular musculoskeletal infection. Top Magn 48:71–82.
Reson Imaging. 2007;18:177–191.
660