Page 155 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 155
Thyroid and Parathyroid 145
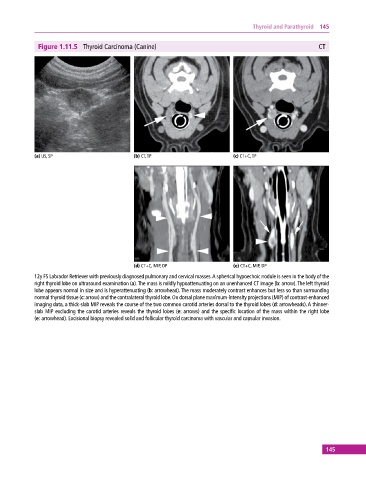
Figure 1.11.5 Thyroid Carcinoma (Canine) CT
(a) US, SP (b) CT, TP (c) CT+C, TP
(d) CT+C, MIP, DP (e) CT+C, MIP, DP
12y FS Labrador Retriever with previously diagnosed pulmonary and cervical masses. A spherical hypoechoic nodule is seen in the body of the
right thyroid lobe on ultrasound examination (a). The mass is mildly hypoattenuating on an unenhanced CT image (b: arrow). The left thyroid
lobe appears normal in size and is hyperattenuating (b: arrowhead). The mass moderately contrast enhances but less so than surrounding
normal thyroid tissue (c: arrow) and the contralateral thyroid lobe. On dorsal plane maximum‐intensity projections (MIP) of contrast‐enhanced
imaging data, a thick‐slab MIP reveals the course of the two common carotid arteries dorsal to the thyroid lobes (d: arrowheads). A thinner‐
slab MIP excluding the carotid arteries reveals the thyroid lobes (e: arrows) and the specific location of the mass within the right lobe
(e: arrowhead). Excisional biopsy revealed solid and follicular thyroid carcinoma with vascular and capsular invasion.
145