Page 221 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 221
Infectious Inflammatory Disorders 211
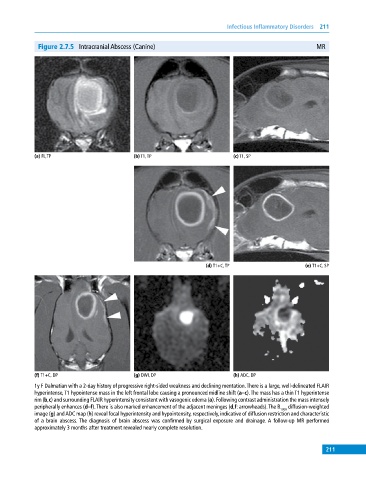
Figure 2.7.5 Intracranial Abscess (Canine) MR
(a) FL,TP (b) T1, TP (c) T1, SP
(d) T1+C, TP (e) T1+C, SP
(f) T1+C, DP (g) DWI, DP (h) ADC, DP
1y F Dalmatian with a 2‐day history of progressive right‐sided weakness and declining mentation. There is a large, well‐delineated FLAIR
hyperintense, T1 hypointense mass in the left frontal lobe causing a pronounced midline shift (a–c). The mass has a thin T1 hyperintense
rim (b,c) and surrounding FLAIR hyperintensity consistent with vasogenic edema (a). Following contrast administration the mass intensely
peripherally enhances (d–f). There is also marked enhancement of the adjacent meninges (d,f: arrowheads). The B 1000 diffusion‐weighted
image (g) and ADC map (h) reveal focal hyperintensity and hypointensity, respectively, indicative of diffusion restriction and characteristic
of a brain abscess. The diagnosis of brain abscess was confirmed by surgical exposure and drainage. A follow‐up MR performed
approximately 3 months after treatment revealed nearly complete resolution.
211