Page 49 - Internal Auditing Standards
P. 49
Guide to Using International Standards on Auditing in the Audits of Small- and Medium-Sized Entities Volume 1—Core Concepts
4.6 Control Activities
Control activities are designed to ensure compliance with the firm’s established policies and procedures.
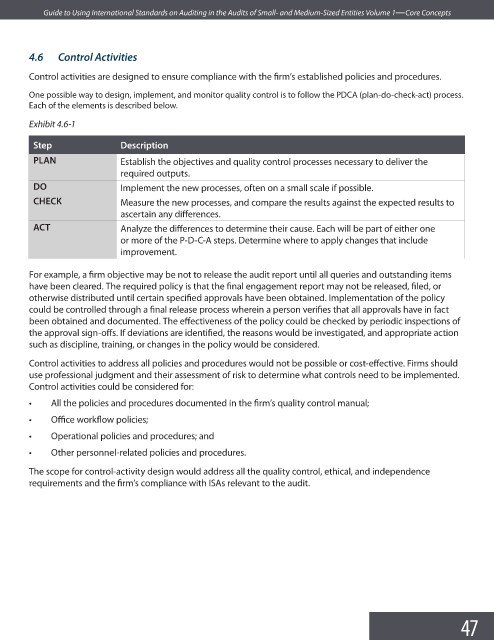
One possible way to design, implement, and monitor quality control is to follow the PDCA (plan-do-check-act) process.
Each of the elements is described below.
Exhibit 4.6-1
Step Description
PLAN Establish the objectives and quality control processes necessary to deliver the
required outputs.
DO Implement the new processes, often on a small scale if possible.
CHECK Measure the new processes, and compare the results against the expected results to
ascertain any diff erences.
ACT Analyze the differences to determine their cause. Each will be part of either one
or more of the P-D-C-A steps. Determine where to apply changes that include
improvement.
For example, a firm objective may be not to release the audit report until all queries and outstanding items
have been cleared. The required policy is that the final engagement report may not be released, fi led, or
otherwise distributed until certain specified approvals have been obtained. Implementation of the policy
could be controlled through a final release process wherein a person verifies that all approvals have in fact
been obtained and documented. The effectiveness of the policy could be checked by periodic inspections of
the approval sign-offs. If deviations are identified, the reasons would be investigated, and appropriate action
such as discipline, training, or changes in the policy would be considered.
Control activities to address all policies and procedures would not be possible or cost-effective. Firms should
use professional judgment and their assessment of risk to determine what controls need to be implemented.
Control activities could be considered for:
• All the policies and procedures documented in the firm’s quality control manual;
• Offi ce workfl ow policies;
• Operational policies and procedures; and
• Other personnel-related policies and procedures.
The scope for control-activity design would address all the quality control, ethical, and independence
requirements and the firm’s compliance with ISAs relevant to the audit.
47