Page 573 - ITGC_Audit Guides
P. 573
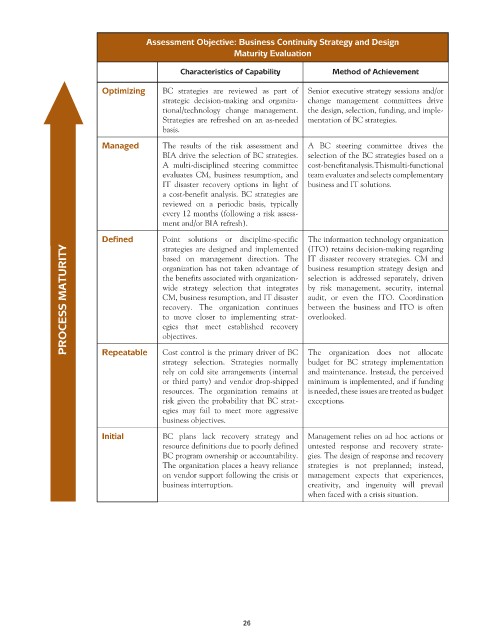
Assessment Objective: Business Continuity Strategy and Design
Maturity Evaluation
Characteristics of Capability Method of Achievement
Optimizing BC strategies are reviewed as part of Senior executive strategy sessions and/or
strategic decision-making and organiza- change management committees drive
tional/technology change management. the design, selection, funding, and imple-
Strategies are refreshed on an as-needed mentation of BC strategies.
basis.
Managed The results of the risk assessment and A BC steering committee drives the
BIA drive the selection of BC strategies. selection of the BC strategies based on a
A multi-disciplined steering committee cost-benefit analysis. This multi-functional
evaluates CM, business resumption, and team evaluates and selects complementary
IT disaster recovery options in light of business and IT solutions.
a cost-benefit analysis. BC strategies are
reviewed on a periodic basis, typically
every 12 months (following a risk assess-
ment and/or BIA refresh).
Defined Point solutions or discipline-specific The information technology organization
strategies are designed and implemented (ITO) retains decision-making regarding
PROCESS MATURITY egies that meet established recovery selection is addressed separately, driven
based on management direction. The IT disaster recovery strategies. CM and
organization has not taken advantage of business resumption strategy design and
the benefits associated with organization-
wide strategy selection that integrates by risk management, security, internal
CM, business resumption, and IT disaster audit, or even the ITO. Coordination
recovery. The organization continues between the business and ITO is often
overlooked.
to move closer to implementing strat-
objectives.
Repeatable
Cost control is the primary driver of BC The organization does not allocate
strategy selection. Strategies normally budget for BC strategy implementation
rely on cold site arrangements (internal and maintenance. Instead, the perceived
or third party) and vendor drop-shipped minimum is implemented, and if funding
resources. The organization remains at is needed, these issues are treated as budget
risk given the probability that BC strat- exceptions.
egies may fail to meet more aggressive
business objectives.
Initial BC plans lack recovery strategy and Management relies on ad hoc actions or
resource definitions due to poorly defined untested response and recovery strate-
BC program ownership or accountability. gies. The design of response and recovery
The organization places a heavy reliance strategies is not preplanned; instead,
on vendor support following the crisis or management expects that experiences,
business interruption. creativity, and ingenuity will prevail
when faced with a crisis situation.
26