Page 574 - ITGC_Audit Guides
P. 574
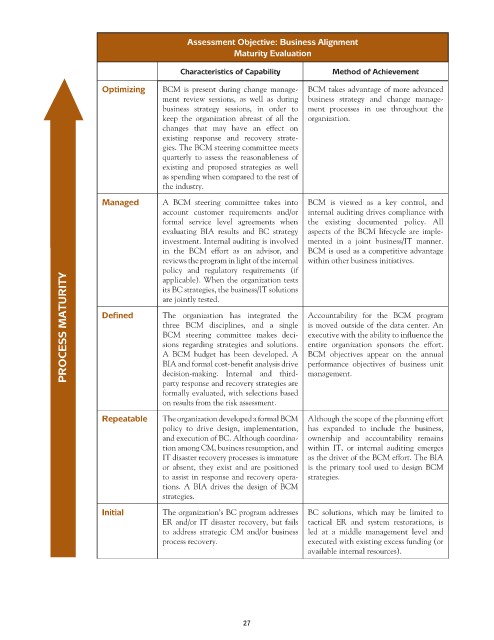
Assessment Objective: Business Alignment
Maturity Evaluation
Characteristics of Capability Method of Achievement
Optimizing BCM is present during change manage- BCM takes advantage of more advanced
ment review sessions, as well as during business strategy and change manage-
business strategy sessions, in order to ment processes in use throughout the
keep the organization abreast of all the organization.
changes that may have an effect on
existing response and recovery strate-
gies. The BCM steering committee meets
quarterly to assess the reasonableness of
existing and proposed strategies as well
as spending when compared to the rest of
the industry.
Managed A BCM steering committee takes into BCM is viewed as a key control, and
account customer requirements and/or internal auditing drives compliance with
formal service level agreements when the existing documented policy. All
evaluating BIA results and BC strategy aspects of the BCM lifecycle are imple-
investment. Internal auditing is involved mented in a joint business/IT manner.
in the BCM effort as an advisor, and BCM is used as a competitive advantage
reviews the program in light of the internal within other business initiatives.
policy and regulatory requirements (if
PROCESS MATURITY Defined sions regarding strategies and solutions. entire organization sponsors the effort.
applicable). When the organization tests
its BC strategies, the business/IT solutions
are jointly tested.
The organization has integrated the Accountability for the BCM program
three BCM disciplines, and a single is moved outside of the data center. An
executive with the ability to influence the
BCM steering committee makes deci-
A BCM budget has been developed. A BCM objectives appear on the annual
BIA and formal cost-benefit analysis drive performance objectives of business unit
decision-making. Internal and third-
party response and recovery strategies are
formally evaluated, with selections based management.
on results from the risk assessment.
Repeatable The organization developed a formal BCM Although the scope of the planning effort
policy to drive design, implementation, has expanded to include the business,
and execution of BC. Although coordina- ownership and accountability remains
tion among CM, business resumption, and within IT, or internal auditing emerges
IT disaster recovery processes is immature as the driver of the BCM effort. The BIA
or absent, they exist and are positioned is the primary tool used to design BCM
to assist in response and recovery opera- strategies.
tions. A BIA drives the design of BCM
strategies.
Initial The organization’s BC program addresses BC solutions, which may be limited to
ER and/or IT disaster recovery, but fails tactical ER and system restorations, is
to address strategic CM and/or business led at a middle management level and
process recovery. executed with existing excess funding (or
available internal resources).
27