Page 132 - Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Disorders in Small Animal Practice
P. 132
122 ELECTROLYTE DISORDERS
intracellular iCa concentration, which controls PTH
and calcitonin secretion. Ionized magnesium (iMg) is
also an agonist of the iCa receptor. Stimulation of the
iCa receptor caused by increased extracellular iCa concen-
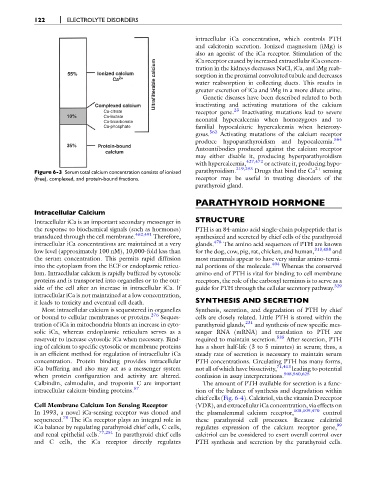
Ultrafilterable calcium water reabsorption in collecting ducts. This results in
55% Ionized calcium tration in the kidneys decreases NaCl, iCa, and iMg reab-
sorption in the proximal convoluted tubule and decreases
Ca 2+
greater excretion of iCa and iMg in a more dilute urine.
Genetic diseases have been described related to both
Complexed calcium inactivating and activating mutations of the calcium
Ca-citrate receptor gene. 23 Inactivating mutations lead to severe
10% Ca-lactate
Ca-bicarbonate neonatal hypercalcemia when homozygous and to
Ca-phosphate familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia when heterozy-
gous. 562 Activating mutations of the calcium receptor
produce hypoparathyroidism and hypocalcemia. 564
35% Protein-bound
calcium Autoantibodies produced against the calcium receptor
may either disable it, producing hyperparathyroidism
with hypercalcemia, 427,472 or activate it, producing hypo-
Figure 6-3 Serum total calcium concentration consists of ionized parathyroidism. 219,293 Drugs that bind the Ca 2þ- sensing
(free), complexed, and protein-bound fractions. receptor may be useful in treating disorders of the
parathyroid gland.
PARATHYROID HORMONE
Intracellular Calcium
STRUCTURE
Intracellular iCa is an important secondary messenger in
the response to biochemical signals (such as hormones) PTH is an 84-amino acid single-chain polypeptide that is
transduced through the cell membrane. 462,491 Therefore, synthesized and secreted by chief cells of the parathyroid
intracellular iCa concentrations are maintained at a very glands. 478 The amino acid sequences of PTH are known
low level (approximately 100 nM), 10,000-fold less than for the dog, cow, pig, rat, chicken, and human, 313,488 and
the serum concentration. This permits rapid diffusion most mammals appear to have very similar amino-termi-
into the cytoplasm from the ECF or endoplasmic reticu- nal portions of the molecule. 404 Whereas the conserved
lum. Intracellular calcium is rapidly buffered by cytosolic amino end of PTH is vital for binding to cell membrane
proteins and is transported into organelles or to the out- receptors, the role of the carboxyl terminus is to serve as a
side of the cell after an increase in intracellular iCa. If guide for PTH through the cellular secretory pathway. 329
intracellular iCa is not maintained at a low concentration,
it leads to toxicity and eventual cell death. SYNTHESIS AND SECRETION
Most intracellular calcium is sequestered in organelles Synthesis, secretion, and degradation of PTH by chief
or bound to cellular membranes or proteins. 276 Seques- cells are closely related. Little PTH is stored within the
tration of iCa in mitochondria blunts an increase in cyto- parathyroid glands, 231 and synthesis of new specific mes-
solic iCa, whereas endoplasmic reticulum serves as a senger RNA (mRNA) and translation to PTH are
reservoir to increase cytosolic iCa when necessary. Bind- required to maintain secretion. 535 After secretion, PTH
ing of calcium to specific cytosolic or membrane proteins has a short half-life (3 to 5 minutes) in serum; thus, a
is an efficient method for regulation of intracellular iCa steady rate of secretion is necessary to maintain serum
concentration. Protein binding provides intracellular PTH concentrations. Circulating PTH has many forms,
iCa buffering and also may act as a messenger system not all of which have bioactivity, 71,413 leading to potential
when protein configuration and activity are altered. confusion in assay interpretations. 508,560,625
Calbindin, calmodulin, and troponin C are important The amount of PTH available for secretion is a func-
intracellular calcium-binding proteins. 57 tion of the balance of synthesis and degradation within
chief cells (Fig. 6-4). Calcitriol, via the vitamin D receptor
Cell Membrane Calcium Ion Sensing Receptor (VDR), and extracellular iCa concentration, via effects on
In 1993, a novel iCa-sensing receptor was cloned and the plasmalemmal calcium receptor, 108,109,470 control
sequenced. 78 The iCa receptor plays an integral role in these parathyroid cell processes. Because calcitriol
iCa balance by regulating parathyroid chief cells, C cells, regulates expression of the calcium receptor gene, 99
and renal epithelial cells. 77,251 In parathyroid chief cells calcitriol can be considered to exert overall control over
and C cells, the iCa receptor directly regulates PTH synthesis and secretion by the parathyroid cells.