Page 535 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 535
502 SECTION | VI Insecticides
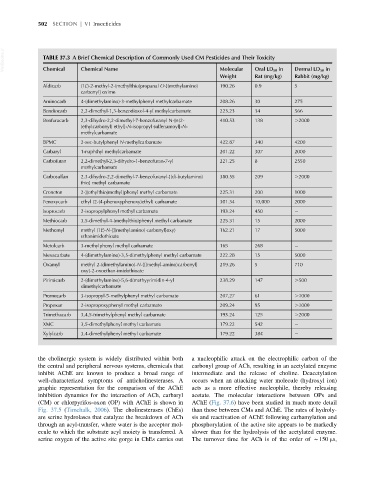
VetBooks.ir TABLE 37.3 A Brief Chemical Description of Commonly Used CM Pesticides and Their Toxicity
Molecular
Chemical Name
Chemical
Rat (mg/kg)
Rabbit (mg/kg)
Weight Oral LD 50 in Dermal LD 50 in
Aldicarb (1E)-2-methyl-2-(methylthio)propanal O-[(methylamino) 190.26 0.9 5
carbonyl] oxime
Aminocarb 4-(dimethylamino)-3-methylphenyl methylcarbamate 208.26 30 275
Bendiocarb 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-benzodioxol-4-yl methylcarbamate 223.23 34 566
Benfuracarb 2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-7-benzofuranyl N-[n[2- 410.53 138 .2000
(ethylcarbonyl) ethyl]-N-isopropyl sulfenamoyl]-N-
methylcarbamate
BPMC 2-sec-butylphenyl N-methylcarbamate 422.87 340 4200
Carbaryl 1-naphthyl methylcarbamate 201.22 307 2000
Carbofuran 2,2-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-7-yl 221.25 8 2550
methylcarbamate
Carbosulfan 2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-7-benzofuranyl-[(di-butylamino) 380.55 209 .2000
thio] methyl carbamate
Croneton 2-[(ethylthio)methyl]phenyl methyl carbamate 225.31 200 1000
Fenoxycarb ethyl [2-(4-phenoxyphenoxy)ethyl] carbamate 301.34 10,000 2000
Isoprocarb 2-isopropylphenyl methyl carbamate 193.24 450
Methiocarb 3,5-dimethyl-4-(methylthio)phenyl methyl carbamate 225.31 15 2000
Methomyl methyl (1E)-N-{[(methylamino) carbonyl]oxy} 162.21 17 5000
ethanimidothioate
Metolcarb 3-methylphenyl methyl carbamate 165 268
Mexacarbate 4-(dimethylamino)-3,5-dimethylphenyl methyl carbamate 222.28 15 5000
Oxamyl methyl 2-(dimethylamino)-N-{[(methyl-amino)carbonyl] 219.26 5 710
oxy}-2-oxoethan-imidothioate
Pirimicarb 2-(dimethylamino)-5,6-dimethyyrimidin-4-yl 238.29 147 .500
dimethylcarbamate
Promecarb 3-isopropyl-5-methylphenyl methyl carbamate 207.27 61 .1000
Propoxur 2-isopropoxyphenyl methyl carbamate 209.24 95 .1000
Trimethacarb 3,4,5-trimethylphenyl methyl carbamate 193.24 125 .2000
XMC 3,5-dimethylphenyl methyl carbamate 179.22 542
Xylylcarb 3,4-dimethylphenyl methyl carbamate 179.22 384
the cholinergic system is widely distributed within both a nucleophilic attack on the electrophilic carbon of the
the central and peripheral nervous systems, chemicals that carbonyl group of ACh, resulting in an acetylated enzyme
inhibit AChE are known to produce a broad range of intermediate and the release of choline. Deacetylation
well-characterized symptoms of anticholinesterases. A occurs when an attacking water molecule (hydroxyl ion)
graphic representation for the comparison of the AChE acts as a more effective nucleophile, thereby releasing
inhibition dynamics for the interaction of ACh, carbaryl acetate. The molecular interactions between OPs and
(CM) or chlorpyrifos-oxon (OP) with AChE is shown in AChE (Fig. 37.6) have been studied in much more detail
Fig. 37.5 (Timchalk, 2006). The cholinesterases (ChEs) than those between CMs and AChE. The rates of hydroly-
are serine hydrolases that catalyze the breakdown of ACh sis and reactivation of AChE following carbamylation and
through an acyl-transfer, where water is the acceptor mol- phosphorylation of the active site appears to be markedly
ecule to which the substrate acyl moiety is transferred. A slower than for the hydrolysis of the acetylated enzyme.
serine oxygen of the active site gorge in ChEs carries out The turnover time for ACh is of the order of B150 μs,