Page 536 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 536
Organophosphates and Carbamates Chapter | 37 503
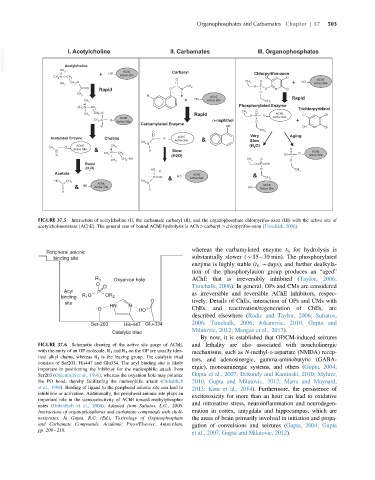
VetBooks.ir Acetylcholine II. Carbamates III. Organophosphates
I. Acetylcholine
+ CH 3 + HO AChE Carbaryl Chlorpyrifos-oxon
CH 3 N Active Site
CH 2 CI CI
O AChE
–O CH 3 O HO
CH 2 +
CH 3 Active Site
CH 3 O P
O O N O N
Rapid CI
O
CH 3
H H AChE
+ HO Rapid
CH 3 Active Site CH 3
+ Phosphorylated Enzyme
CH 3 N CH 2 Trichlorpyridinol
O
CH 2 –O
CH 3
CH 3 Rapid O P O AChE CI CI
AChE Active Site
CH 3 –C O– Active Site α-naphthol O +
Carbamylated Enzyme
–O OH OH N CI
O CH 3
Acetylated Enzyme Choline C O AChE Very Aging
Active Site & Slow
CH 3 N
AChE CH 3 (H 2 O)
CH 3 O
Active Site & + H Slow O AChE
CH 3 N CH 2 O
O (H2O) OH P Active Site
–OH O
CH 2 CH 3
CH 3 O
Rapid O P OH
(H 2 O)
HO C O CH 3
Acetate AChE
C O & HO Active Site & CH 3
HO CH 3 CH 3 N
C HO AChE AChE
& Active Site HO Active Site
O H
FIGURE 37.5 Interaction of acetylcholine (I), the carbamate carbaryl (II), and the organophosphate chlorpyrifos-oxon (III) with the active site of
acetylcholinesterase (AChE). The general rate of bound AChE hydrolysis is ACh . carbaryl . chlorpyrifos-oxon (Timchalk, 2006).
whereas the carbamylated enzyme t 1 /2 for hydrolysis is
Peripheral anionic
binding site substantially slower (B15 30 min). The phosphorylated
enzyme is highly stable (t 1 /2 Bdays), and further dealkyla-
tion of the phosphorylation group produces an “aged”
R 3 Oxyanion hole AChE that is irreversibly inhibited (Taylor, 2006;
O
O Timchalk, 2006). In general, OPs and CMs are considered
Acyl P
binding R 1 O OR 2 as irreversible and reversible AChE inhibitors, respec-
site HN N O tively. Details of ChEs, interaction of OPs and CMs with
– O HO ChEs, and reactivation/regeneration of ChEs, are
described elsewhere (Radic and Taylor, 2006; Sultatos,
Ser-203 His-447 Glu-334 2006; Timchalk, 2006; Jokanovic, 2010; Gupta and
Milatovic, 2012; Mangas et al., 2017).
Catalytic triad
By now, it is established that OP/CM-induced seizures
FIGURE 37.6 Schematic drawing of the active site gorge of AChE, and lethality are also associated with noncholinergic
with the entry of an OP molecule. R 1 and R 2 on the OP are usually iden- mechanisms, such as N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) recep-
tical alkyl chains, whereas R 3 is the leaving group. The catalytic triad tors, and adenosinergic, gamma-aminobutyric (GABA-
consists of Ser203, His447 and Glu334. The acyl binding site is likely
ergic), monoaminergic systems, and others (Gupta, 2004;
important in positioning the inhibitor for the nucleophilic attack from
Ser203 (Ordentlich et al., 1996), whereas the oxyanion hole may polarize Gupta et al., 2007; Dekundy and Kaminski, 2010; Myhrer,
the PO bond, thereby facilitating the nucleophilic attack (Ordentlich 2010; Gupta and Milatovic, 2012; Marrs and Maynard,
et al., 1998). Binding of ligand to the peripheral anionic site can lead to 2013; Kaur et al., 2014). Furthermore, the persistence of
inhibition or activation. Additionally, the peripheral anionic site plays an
excitotoxicity for more than an hour can lead to oxidative
important role in the stereoselectivity of AChE toward methylphospho-
and nitrosative stress, neuroinflammation and neurodegen-
nates (Ordentlich et al., 2004). Adapted from Sultatos, L.G., 2006.
Interactions of organophosphorus and carbamate compounds with choli- eration in cortex, amygdala and hippocampus, which are
nesterases. In Gupta, R.C. (Ed.), Toxicology of Organophosphate the areas of brain primarily involved in initiation and propa-
and Carbamate Compounds. Academic Press/Elsevier, Amsterdam, gation of convulsions and seizures (Gupta, 2004; Gupta
pp. 209 218.
et al., 2007; Gupta and Milatovic, 2012).