Page 334 - Linear Models for the Prediction of Animal Breeding Values 3rd Edition
P. 334
Appendix E
E.1 Canonical Transformation: Procedure to Calculate
the Transformation Matrix and its Inverse
The simplification of a multivariate analysis into n single trait analyses using canoni-
cal transformation involves transforming the observations of several correlated traits
into new uncorrected traits (Section 6.2). The transformation matrix Q can be calcu-
lated by the following procedure, which has been illustrated by the G and R matrices
for Example 6.1 in Section 6.2.2.
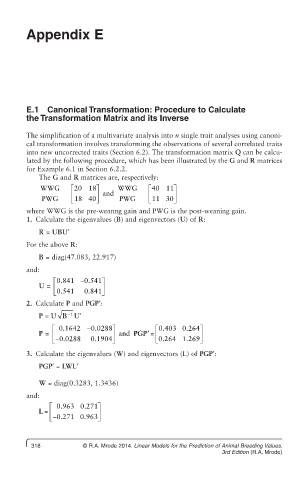
The G and R matrices are, respectively:
WWG é 20 18ù WWG é 40 11ù
ê ú and ê ú
PWG ë 18 40 û PWG ë 11 30 û
where WWG is the pre-weanng gain and PWG is the post-weaning gain.
1. Calculate the eigenvalues (B) and eigenvectors (U) of R:
R = UBU′
For the above R:
B = diag(47.083, 22.917)
and:
é 0.841 - 0.541ù
U = ê ú
ë 0.541 0.841 û
2. Calculate P and PGP′:
P = U B −1 U′
é 0.1642 - 0.0288ù é 0.403 0.264ù
P = ê ú and PG P′ = ê ú
ë - 0.0288 0.1904 û ë 0.2264 1.269 û
3. Calculate the eigenvalues (W) and eigenvectors (L) of PGP′:
PGP′ = LWL′
W = diag(0.3283, 1.3436)
and:
é 0.963 0.271ù
L = ê ú
ë - 0.271 0.963 û
318 © R.A. Mrode 2014. Linear Models for the Prediction of Animal Breeding Values,
3rd Edition (R.A. Mrode)