Page 195 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 195
198 12 Congenital Heart Disease
(e)
(f)
(g) (h)
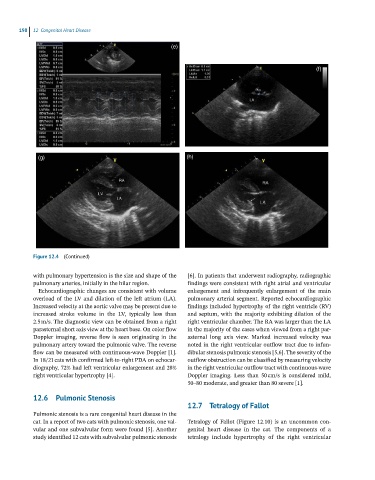
Figure 12.4 (Continued)
with pulmonary hypertension is the size and shape of the [6]. In patients that underwent radiography, radiographic
pulmonary arteries, initially in the hilar region. findings were consistent with right atrial and ventricular
Echocardiographic changes are consistent with volume enlargement and infrequently enlargement of the main
overload of the LV and dilation of the left atrium (LA). pulmonary arterial segment. Reported echocardiographic
Increased velocity at the aortic valve may be present due to findings included hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV)
increased stroke volume in the LV, typically less than and septum, with the majority exhibiting dilation of the
2.5 m/s. The diagnostic view can be obtained from a right right ventricular chamber. The RA was larger than the LA
parasternal short axis view at the heart base. On color flow in the majority of the cases when viewed from a right par-
Doppler imaging, reverse flow is seen originating in the asternal long axis view. Marked increased velocity was
pulmonary artery toward the pulmonic valve. The reverse noted in the right ventricular outflow tract due to infun-
flow can be measured with continuous‐wave Doppler [1]. dibular stenosis pulmonic stenosis [5,6]. The severity of the
In 18/21 cats with confirmed left‐to‐right PDA on echocar- outflow obstruction can be classified by measuring velocity
diography, 72% had left ventricular enlargement and 28% in the right ventricular outflow tract with continuous‐wave
right ventricular hypertrophy [4]. Doppler imaging. Less than 50 cm/s is considered mild,
50–80 moderate, and greater than 80 severe [1].
12.6 Pulmonic Stenosis
12.7 Tetralogy of Fallot
Pulmonic stenosis is a rare congenital heart disease in the
cat. In a report of two cats with pulmonic stenosis, one val- Tetralogy of Fallot (Figure 12.10) is an uncommon con-
vular and one subvalvular form were found [5]. Another genital heart disease in the cat. The components of a
study identified 12 cats with subvalvular pulmonic stenosis tetralogy include hypertrophy of the right ventricular