Page 24 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 24
2.3 Computed Tomography 17
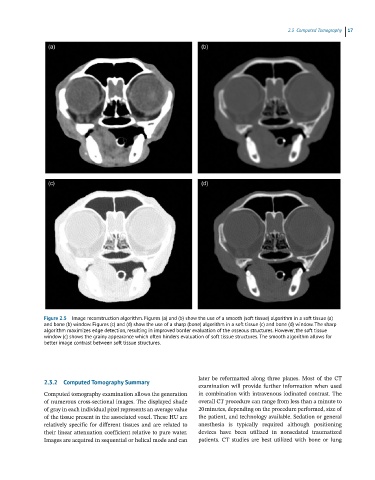
Figure 2.5 Image reconstruction algorithm. Figures (a) and (b) show the use of a smooth (soft tissue) algorithm in a soft tissue (a)
and bone (b) window. Figures (c) and (d) show the use of a sharp (bone) algorithm in a soft tissue (c) and bone (d) window. The sharp
algorithm maximizes edge detection, resulting in improved border evaluation of the osseous structures. However, the soft tissue
window (c) shows the grainy appearance which often hinders evaluation of soft tissue structures. The smooth algorithm allows for
better image contrast between soft tissue structures.
later be reformatted along three planes. Most of the CT
2.3.2 Computed Tomography Summary
examination will provide further information when used
Computed tomography examination allows the generation in combination with intravenous iodinated contrast. The
of numerous cross‐sectional images. The displayed shade overall CT procedure can range from less than a minute to
of gray in each individual pixel represents an average value 20 minutes, depending on the procedure performed, size of
of the tissue present in the associated voxel. These HU are the patient, and technology available. Sedation or general
relatively specific for different tissues and are related to anesthesia is typically required although positioning
their linear attenuation coefficient relative to pure water. devices have been utilized in nonsedated traumatized
Images are acquired in sequential or helical mode and can patients. CT studies are best utilized with bone or lung