Page 28 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 28
2.4 Magnetic Resonance Imaging 21
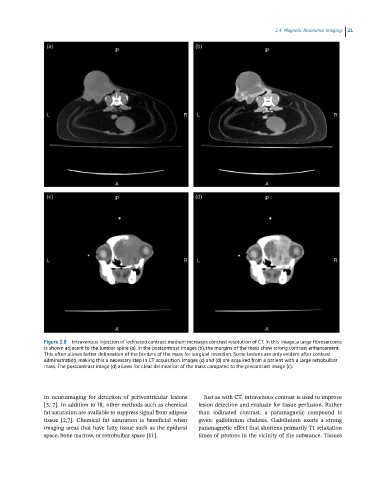
Figure 2.8 Intravenous injection of iodinated contrast medium increases contrast resolution of CT. In this image, a large fibrosarcoma
is shown adjacent to the lumbar spine (a). In the postcontrast images (b), the margins of the mass show strong contrast enhancement.
This often allows better delineation of the borders of the mass for surgical resection. Some lesions are only evident after contrast
administration, making this a necessary step in CT acquisition. Images (c) and (d) are acquired from a patient with a large retrobulbar
mass. The postcontrast image (d) allows for clear delineation of the mass compared to the precontrast image (c).
in neuroimaging for detection of periventricular lesions Just as with CT, intravenous contrast is used to improve
[3, 7]. In addition to IR, other methods such as chemical lesion detection and evaluate for tissue perfusion. Rather
fat saturation are available to suppress signal from adipose than iodinated contrast, a paramagnetic compound is
tissue [2,7]. Chemical fat saturation is beneficial when given: gadolinium chelates. Gadolinium exerts a strong
imaging areas that have fatty tissue such as the epidural paramagnetic effect that shortens primarily T1 relaxation
space, bone marrow, or retrobulbar space [11]. times of protons in the vicinity of the substance. Tissues