Page 293 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 293
17.2 Mediastinal Masses 297
(a) (b)
(c)
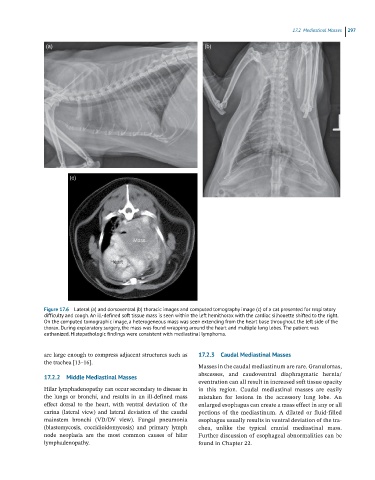
Figure 17.6 Lateral (a) and dorsoventral (b) thoracic images and computed tomography image (c) of a cat presented for respiratory
difficulty and cough. An ill-defined soft tissue mass is seen within the left hemithorax with the cardiac silhouette shifted to the right.
On the computed tomographic image, a heterogeneous mass was seen extending from the heart base throughout the left side of the
thorax. During exploratory surgery, the mass was found wrapping around the heart and multiple lung lobes. The patient was
euthanized. Histopathologic findings were consistent with mediastinal lymphoma.
are large enough to compress adjacent structures such as 17.2.3 Caudal Mediastinal Masses
the trachea [13–16].
Masses in the caudal mediastinum are rare. Granulomas,
17.2.2 Middle Mediastinal Masses abscesses, and caudoventral diaphragmatic hernia/
eventration can all result in increased soft tissue opacity
Hilar lymphadenopathy can occur secondary to disease in in this region. Caudal mediastinal masses are easily
the lungs or bronchi, and results in an ill‐defined mass mistaken for lesions in the accessory lung lobe. An
effect dorsal to the heart, with ventral deviation of the enlarged esophagus can create a mass effect in any or all
carina (lateral view) and lateral deviation of the caudal portions of the mediastinum. A dilated or fluid‐filled
mainstem bronchi (VD/DV view). Fungal pneumonia esophagus usually results in ventral deviation of the tra-
(blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis) and primary lymph chea, unlike the typical cranial mediastinal mass.
node neoplasia are the most common causes of hilar Further discussion of esophageal abnormalities can be
lymphadenopathy. found in Chapter 22.