Page 294 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 294
298 17 Mediastinal Disease
(a) (b)
(c)
(d)
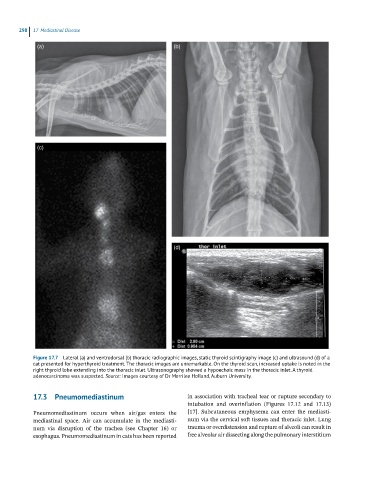
Figure 17.7 Lateral (a) and ventrodorsal (b) thoracic radiographic images, static thyroid scintigraphy image (c) and ultrasound (d) of a
cat presented for hyperthyroid treatment. The thoracic images are unremarkable. On the thyroid scan, increased uptake is noted in the
right thyroid lobe extending into the thoracic inlet. Ultrasonography showed a hypoechoic mass in the thoracic inlet. A thyroid
adenocarcinoma was suspected. Source: Images courtesy of Dr Merrilee Holland, Auburn University.
17.3 Pneumomediastinum in association with tracheal tear or rupture secondary to
intubation and overinflation (Figures 17.12 and 17.13)
Pneumomediastinum occurs when air/gas enters the [17]. Subcutaneous emphysema can enter the mediasti-
mediastinal space. Air can accumulate in the mediasti- num via the cervical soft tissues and thoracic inlet. Lung
num via disruption of the trachea (see Chapter 16) or trauma or overdistension and rupture of alveoli can result in
esophagus. Pneumomediastinum in cats has been reported free alveolar air dissecting along the pulmonary interstitium