Page 36 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 36
3.5 Image isplay 29
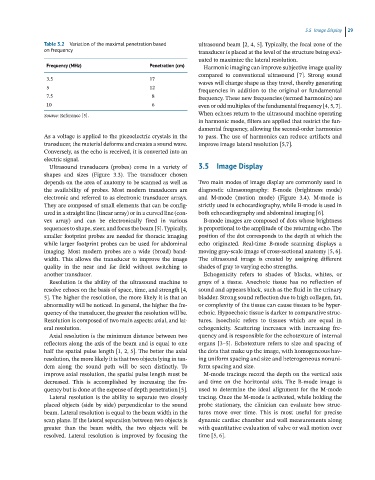
Table 3.2 Variation of the maximal penetration based ultrasound beam [2, 4, 5]. Typically, the focal zone of the
on frequency transducer is placed at the level of the structure being eval-
uated to maximize the lateral resolution.
Frequency (MHz) Penetration (cm) Harmonic imaging can improve subjective image quality
compared to conventional ultrasound [7]. Strong sound
3.5 17 waves will change shape as they travel, thereby generating
5 12 frequencies in addition to the original or fundamental
7.5 8 frequency. These new frequencies (termed harmonics) are
10 6 even or odd multiples of the fundamental frequency [4, 5, 7].
Source: Reference [5]. When echoes return to the ultrasound machine operating
in harmonic mode, filters are applied that restrict the fun-
damental frequency, allowing the second‐order harmonics
As a voltage is applied to the piezoelectric crystals in the to pass. The use of harmonics can reduce artifacts and
transducer, the material deforms and creates a sound wave. improve image lateral resolution [5,7].
Conversely, as the echo is received, it is converted into an
electric signal.
Ultrasound transducers (probes) come in a variety of 3.5 Image Display
shapes and sizes (Figure 3.3). The transducer chosen
depends on the area of anatomy to be scanned as well as Two main modes of image display are commonly used in
the availability of probes. Most modern transducers are diagnostic ultrasonography: B‐mode (brightness mode)
electronic and referred to as electronic transducer arrays. and M‐mode (motion mode) (Figure 3.4). M‐mode is
They are composed of small elements that can be config- strictly used in echocardiography, while B‐mode is used in
ured in a straight line (linear array) or in a curved line (con- both echocardiography and abdominal imaging [6].
vex array) and can be electronically fired in various B‐mode images are composed of dots whose brightness
sequences to shape, steer, and focus the beam [5]. Typically, is proportional to the amplitude of the returning echo. The
smaller footprint probes are needed for thoracic imaging position of the dot corresponds to the depth at which the
while larger footprint probes can be used for abdominal echo originated. Real‐time B‐mode scanning displays a
imaging. Most modern probes are a wide (broad) band- moving gray‐scale image of cross‐sectional anatomy [5, 6].
width. This allows the transducer to improve the image The ultrasound image is created by assigning different
quality in the near and far field without switching to shades of gray to varying echo strengths.
another transducer. Echogenicity refers to shades of blacks, whites, or
Resolution is the ability of the ultrasound machine to grays of a tissue. Anechoic tissue has no reflection of
resolve echoes on the basis of space, time, and strength [4, sound and appears black, such as the fluid in the urinary
5]. The higher the resolution, the more likely it is that an bladder. Strong sound reflection due to high collagen, fat,
abnormality will be noticed. In general, the higher the fre- or complexity of the tissue can cause tissues to be hyper-
quency of the transducer, the greater the resolution will be. echoic. Hypoechoic tissue is darker to comparative struc-
Resolution is composed of two main aspects: axial, and lat- tures. Isoechoic refers to tissues which are equal in
eral resolution. echogenicity. Scattering increases with increasing fre-
Axial resolution is the minimum distance between two quency and is responsible for the echotexture of internal
reflectors along the axis of the beam and is equal to one organs [3–5]. Echotexture refers to size and spacing of
half the spatial pulse length [1, 2, 5]. The better the axial the dots that make up the image, with homogeneous hav-
resolution, the more likely it is that two objects lying in tan- ing uniform spacing and size and heterogeneous nonuni-
dem along the sound path will be seen distinctly. To form spacing and size.
improve axial resolution, the spatial pulse length must be M‐mode tracings record the depth on the vertical axis
decreased. This is accomplished by increasing the fre- and time on the horizontal axis. The B‐mode image is
quency but is done at the expense of depth penetration [5]. used to determine the ideal alignment for the M‐mode
Lateral resolution is the ability to separate two closely tracing. Once the M‐mode is activated, while holding the
placed objects (side by side) perpendicular to the sound probe stationary, the clinician can evaluate how struc-
beam. Lateral resolution is equal to the beam width in the tures move over time. This is most useful for precise
scan plane. If the lateral separation between two objects is dynamic cardiac chamber and wall measurements along
greater than the beam width, the two objects will be with quantitative evaluation of valve or wall motion over
resolved. Lateral resolution is improved by focusing the time [5, 6].