Page 385 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 385
Receptors and sense organs (organa sensuum) 367
in the chicken), representing the site of highest monocular retina. The axons pass to the main visual relay centre of the
VetBooks.ir visual resolution. In many water- and shore-birds, the cen- brain, the lateral geniculate body. From there, nerve fibres
tral area is linear (termed the area centralis horizontalis) of the visual pathway project to the visual cerebral cortex
in the occipital lobe. Autonomic fibres in the optic nerve
and contains a fovea centralis.
Several diurnal raptors also possess an area temporalis pass to the hypothalamus forming the retinohypothalamic
with a fovea temporalis, which contributes to binocular, tracts (suprachiasmatic nucleus).
stereoscopic vision. Owls have only an area temporalis. Within the nerve fibre layer, the fibres are non-myeli-
In contrast to the retina of most mammals, the avian nated. After penetrating the area cribrosa of the sclera, the
retina is avascular. It receives its nutrition by diffusion axons are surrounded by oligodendrocytes, through which
from the capillary network of the lamina choriocapilla- they become myelinated (Figure 16.30). The autonomic
ris and from the richly vascularised pecten oculi (Figures fibres are poorly myelinated.
16.31 and 16.32). As a component of the brain, the optic nerve is
ensheathed by pia mater, arachnoid and dura mater.
OPTIC NERVE (NERVUS OPTICUS) Distinct subdural and subarachnoid spaces are evident.
The optic nerve (cranial nerve II) is an afferent tract of the At the area cribrosa, the meningeal layers merge with the
brain. The nerve is composed of axons of the multipolar sclera. Numerous connective tissue septa extending from
ganglion cells that initially form the nerve fibre layer of the the pia, accompanied by capillaries, project between the
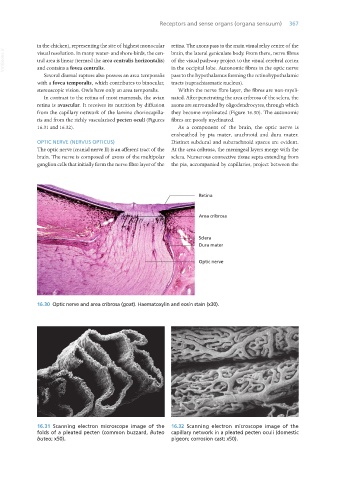
16.30 Optic nerve and area cribrosa (goat). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x30).
16.31 Scanning electron microscope image of the 16.32 Scanning electron microscope image of the
folds of a pleated pecten (common buzzard, Buteo capillary network in a pleated pecten oculi (domestic
buteo; x50). pigeon; corrosion cast; x50).
Vet Histology.indb 367 16/07/2019 15:07