Page 381 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 381
Receptors and sense organs (organa sensuum) 363
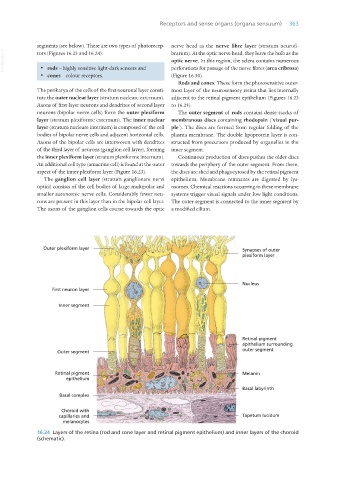
segments (see below). There are two types of photorecep- nerve head as the nerve fibre layer (stratum neurofi-
VetBooks.ir tors (Figures 16.23 and 16.24): brarum). At the optic nerve head, they leave the bulb as the
optic nerve. In this region, the sclera contains numerous
· rods – highly sensitive light-dark sensors and
perforations for passage of the nerve fibres (area cribrosa)
· cones – colour receptors. (Figure 16.30).
Rods and cones: These form the photosensitive outer-
The perikarya of the cells of the first neuronal layer consti- most layer of the neurosensory retina that lies internally
tute the outer nuclear layer (stratum nucleare externum). adjacent to the retinal pigment epithelium (Figures 16.23
Axons of first-layer neurons and dendrites of second layer to 16.25).
neurons (bipolar nerve cells) form the outer plexiform The outer segment of rods contains dense stacks of
layer (stratum plexiforme externum). The inner nuclear membranous discs containing rhodopsin (‘visual pur-
layer (stratum nucleare internum) is composed of the cell ple’). The discs are formed from regular folding of the
bodies of bipolar nerve cells and adjacent horizontal cells. plasma membrane. The double lipoprotein layer is con-
Axons of the bipolar cells are interwoven with dendrites structed from precursors produced by organelles in the
of the third layer of neurons (ganglion cell layer), forming inner segment.
the inner plexiform layer (stratum plexiforme internum). Continuous production of discs pushes the older discs
An additional cell type (amacrine cell) is found at the outer towards the periphery of the outer segment. From there,
aspect of the inner plexiform layer (Figure 16.23). the discs are shed and phagocytosed by the retinal pigment
The ganglion cell layer (stratum ganglionare nervi epithelium. Membrane remnants are digested by lys-
optici) consists of the cell bodies of large multipolar and osomes. Chemical reactions occurring in these membrane
smaller autonomic nerve cells. Considerably fewer neu- systems trigger visual signals under low light conditions.
rons are present in this layer than in the bipolar cell layer. The outer segment is connected to the inner segment by
The axons of the ganglion cells course towards the optic a modified cilium.
16.24 Layers of the retina (rod and cone layer and retinal pigment epithelium) and inner layers of the choroid
(schematic).
Vet Histology.indb 363 16/07/2019 15:07