Page 383 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 383
Receptors and sense organs (organa sensuum) 365
VetBooks.ir
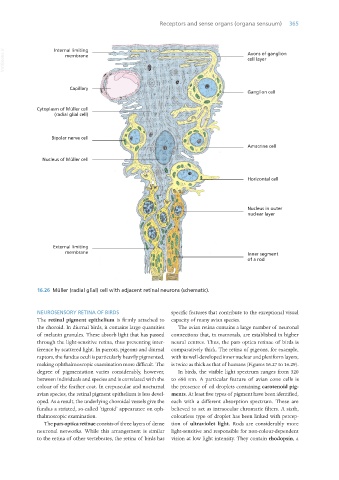
16.26 Müller (radial glial) cell with adjacent retinal neurons (schematic).
NEUROSENSORY RETINA OF BIRDS specific features that contribute to the exceptional visual
The retinal pigment epithelium is firmly attached to capacity of many avian species.
the choroid. In diurnal birds, it contains large quantities The avian retina contains a large number of neuronal
of melanin granules. These absorb light that has passed connections that, in mammals, are established in higher
through the light-sensitive retina, thus preventing inter- neural centres. Thus, the pars optica retinae of birds is
ference by scattered light. In parrots, pigeons and diurnal comparatively thick. The retina of pigeons, for example,
raptors, the fundus oculi is particularly heavily pigmented, with its well-developed inner nuclear and plexiform layers,
making ophthalmoscopic examination more difficult. The is twice as thick as that of humans (Figures 16.27 to 16.29).
degree of pigmentation varies considerably, however, In birds, the visible light spectrum ranges from 320
between individuals and species and is correlated with the to 680 nm. A particular feature of avian cone cells is
colour of the feather coat. In crepuscular and nocturnal the presence of oil droplets containing carotenoid pig-
avian species, the retinal pigment epithelium is less devel- ments. At least five types of pigment have been identified,
oped. As a result, the underlying choroidal vessels give the each with a different absorption spectrum. These are
fundus a striated, so-called ‘tigroid’ appearance on oph- believed to act as intraocular chromatic filters. A sixth,
thalmoscopic examination. colourless type of droplet has been linked with percep-
The pars optica retinae consists of three layers of dense tion of ultraviolet light. Rods are considerably more
neuronal networks. While this arrangement is similar light-sensitive and responsible for non-colour-dependent
to the retina of other vertebrates, the retina of birds has vision at low light intensity. They contain rhodopsin, a
Vet Histology.indb 365 16/07/2019 15:07