Page 30 - eBook T2 eISBN2
P. 30
MANUAL TITLE GOES HERE
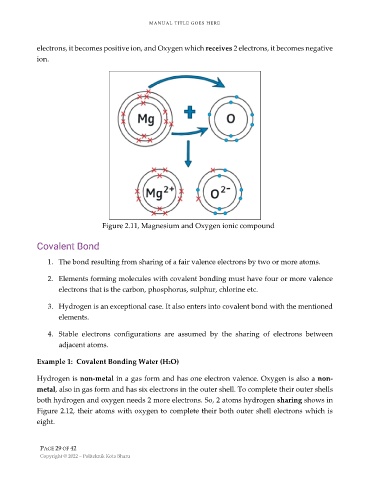
electrons, it becomes positive ion, and Oxygen which receives 2 electrons, it becomes negative
ion.
Figure 2.11, Magnesium and Oxygen ionic compound
Covalent Bond
1. The bond resulting from sharing of a fair valence electrons by two or more atoms.
2. Elements forming molecules with covalent bonding must have four or more valence
electrons that is the carbon, phosphorus, sulphur, chlorine etc.
3. Hydrogen is an exceptional case. It also enters into covalent bond with the mentioned
elements.
4. Stable electrons configurations are assumed by the sharing of electrons between
adjacent atoms.
Example 1: Covalent Bonding Water (H2O)
Hydrogen is non-metal in a gas form and has one electron valence. Oxygen is also a non-
metal, also in gas form and has six electrons in the outer shell. To complete their outer shells
both hydrogen and oxygen needs 2 more electrons. So, 2 atoms hydrogen sharing shows in
Figure 2.12, their atoms with oxygen to complete their both outer shell electrons which is
eight.
PAGE 29 OF 42
Copyright © 2022 – Politeknik Kota Bharu