Page 428 - Microeconomics, Fourth Edition
P. 428
c10competitive markets applications.qxd 7/15/10 4:58 PM Page 402
402 CHAPTER 10 COMPETITIVE MARKETS: APPLICATIONS
Y Y
Rental price (dollars per month) P = $1,600 A U V S X A U V T S X
B
B
E
E
*
F
C
C
F
P = $1,000
R
Z G W D Z G W H D
Q = 50 Q* = 80 Q = 140 Q = 50 80 90 Q = 140
s
d
d
s
Housing shortage Housing shortage
Quantity (thousands of housing units) Quantity (thousands of housing units)
Case 1: Maximum consumer surplus Case 2: Minimum consumer surplus
With Rent Control Impact of Rent Control
Case 1 Case 2 Case 1 Case 2
Free Market (maximum (minimum (maximum (minimum
( with no consumer consumer consumer consumer
r ent control) surplus) surplus) surplus) surplus)
C onsumer surplus A + B + E A + B + C H C – E –A – B – E + H
Producer surplus C + F + G G G –C – F –C – F
Net benefits A + B + C + E + F + G A + B + H + G –E – F –A – B – C –
(c onsumer surplus + C + G E – F + H
producer surplus)
Deadweight loss zero E + F A + B + C + E + F A + B + C + E +
E + F – H F – H
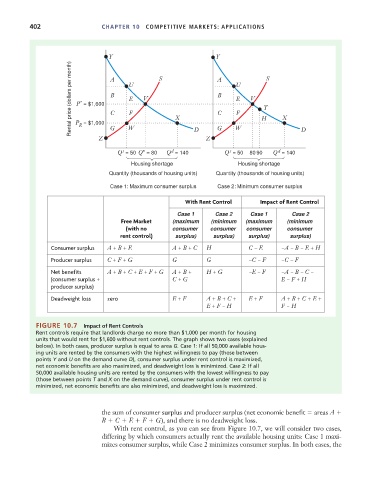
FIGURE 10.7 Impact of Rent Controls
Rent controls require that landlords charge no more than $1,000 per month for housing
units that would rent for $1,600 without rent controls. The graph shows two cases (explained
below). In both cases, producer surplus is equal to area G. Case 1: If all 50,000 available hous-
ing units are rented by the consumers with the highest willingness to pay (those between
points Y and U on the demand curve D), consumer surplus under rent control is maximized,
net economic benefits are also maximized, and deadweight loss is minimized. Case 2: If all
50,000 available housing units are rented by the consumers with the lowest willingness to pay
(those between points T and X on the demand curve), consumer surplus under rent control is
minimized, net economic benefits are also minimized, and deadweight loss is maximized.
the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus (net economic benefit areas A
B C E F G), and there is no deadweight loss.
With rent control, as you can see from Figure 10.7, we will consider two cases,
differing by which consumers actually rent the available housing units: Case 1 maxi-
mizes consumer surplus, while Case 2 minimizes consumer surplus. In both cases, the