Page 486 - Microeconomics, Fourth Edition
P. 486
c11monopolyandmonopsony.qxd 7/14/10 7:58 PM Page 460
460 CHAPTER 11 MONOPOLY AND MONOPSONY
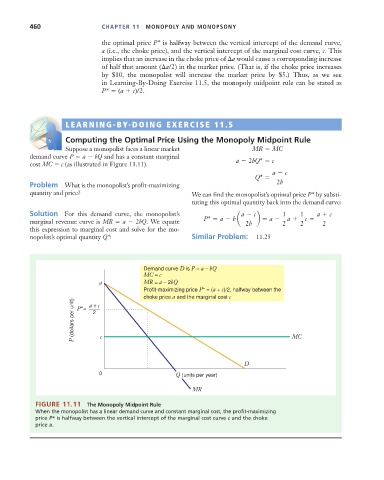
the optimal price P* is halfway between the vertical intercept of the demand curve,
a (i.e., the choke price), and the vertical intercept of the marginal cost curve, c. This
implies that an increase in the choke price of a would cause a corresponding increase
of half that amount ( a/2) in the market price. (That is, if the choke price increases
by $10, the monopolist will increase the market price by $5.) Thus, as we see
in Learning-By-Doing Exercise 11.5, the monopoly midpoint rule can be stated as
P* (a c)/2.
LEARNING-BY-DOING EXERCISE 11.5
S
D
E
Computing the Optimal Price Using the Monopoly Midpoint Rule
Suppose a monopolist faces a linear market MR MC
demand curve P a bQ and has a constant marginal
cost MC c (as illustrated in Figure 11.11). a 2bQ* c
a c
Q*
Problem What is the monopolist’s profit-maximizing 2b
quantity and price? We can find the monopolist’s optimal price P* by substi-
tuting this optimal quantity back into the demand curve:
Solution For this demand curve, the monopolist’s a c 1 1 a c
P* a b a b a a c
marginal revenue curve is MR a 2bQ. We equate 2b 2 2 2
this expression to marginal cost and solve for the mo-
nopolist’s optimal quantity Q*: Similar Problem: 11.25
Demand curve D is P = a – bQ
MC = c
a MR = a – 2bQ
Profit-maximizing price P* = (a + c)/2, halfway between the
choke price a and the marginal cost c
P (dollars per unit) P*= 2 c MC
a + c
D
0 Q (units per year)
MR
FIGURE 11.11 The Monopoly Midpoint Rule
When the monopolist has a linear demand curve and constant marginal cost, the profit-maximizing
price P* is halfway between the vertical intercept of the marginal cost curve c and the choke
price a.