Page 534 - Basic College Mathematics with Early Integers
P. 534
S E C T ION 7.1 I READING PICTOGRAPHS, BAR GRAPHS, HISTOGRAMS, AND LINE GRAPHS 511
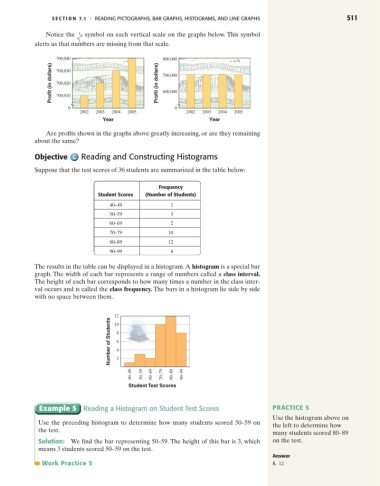
Notice the symbol on each vertical scale on the graphs below. This symbol
alerts us that numbers are missing from that scale.
700,040 800,000
Profit (in dollars) 700,030 Profit (in dollars) 700,000
700,020
600,000
700,010
0 0
2002 2003 2004 2005 2002 2003 2004 2005
Year Year
Are profits shown in the graphs above greatly increasing, or are they remaining
about the same?
Objective Reading and Constructing Histograms
Suppose that the test scores of 36 students are summarized in the table below:
Frequency
Student Scores (Number of Students)
40–49 1
50–59 3
60–69 2
70–79 10
80–89 12
90–99 8
The results in the table can be displayed in a histogram.A histogram is a special bar
graph. The width of each bar represents a range of numbers called a class interval.
The height of each bar corresponds to how many times a number in the class inter-
val occurs and is called the class frequency. The bars in a histogram lie side by side
with no space between them.
12
Number of Students 8 6 4
10
2
40–49 50–59 60–69 70–79 80–89 90–99
Student Test Scores
Example 5 Reading a Histogram on Student Test Scores PRACTICE 5
Use the histogram above on
Use the preceding histogram to determine how many students scored 50–59 on
the left to determine how
the test.
many students scored 80–89
Solution: We find the bar representing 50–59. The height of this bar is 3, which on the test.
means 3 students scored 50–59 on the test.
Answer
Work Practice 5 5. 12