Page 555 - Basic Electrical Engineering
P. 555
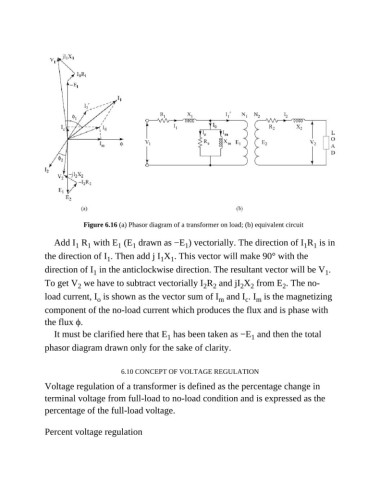
Figure 6.16 (a) Phasor diagram of a transformer on load; (b) equivalent circuit
Add I R with E (E drawn as −E ) vectorially. The direction of I R is in
1
1
1
1
1
1 1
the direction of I . Then add j I X . This vector will make 90° with the
1 1
1
direction of I in the anticlockwise direction. The resultant vector will be V .
1
1
To get V we have to subtract vectorially I R and jI X from E . The no-
2
2 2
2 2
2
load current, I is shown as the vector sum of I and I . I is the magnetizing
c
m
m
o
component of the no-load current which produces the flux and is phase with
the flux ϕ.
It must be clarified here that E has been taken as −E and then the total
1
1
phasor diagram drawn only for the sake of clarity.
6.10 CONCEPT OF VOLTAGE REGULATION
Voltage regulation of a transformer is defined as the percentage change in
terminal voltage from full-load to no-load condition and is expressed as the
percentage of the full-load voltage.
Percent voltage regulation