Page 140 - Fiber Optic Communications Fund
P. 140
Lasers 121
Energy (Arb. unit)
Conduction band
E 1 > E g
E g
Valence band top
k 1
Wavenumber, k
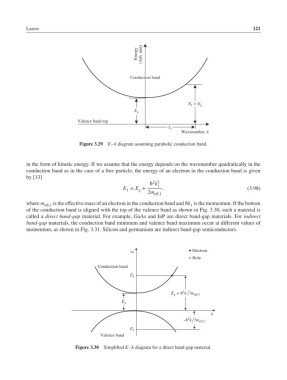
Figure 3.29 E–k diagram assuming parabolic conduction band.
in the form of kinetic energy. If we assume that the energy depends on the wavenumber quadratically in the
conduction band as in the case of a free particle, the energy of an electron in the conduction band is given
by [13]
2 2
ℏ k
E = E + 1 , (3.98)
1 g
2m
eff,1
where m eff,1 is the effective mass of an electron in the conduction band and ℏk is the momentum. If the bottom
1
of the conduction band is aligned with the top of the valence band as shown in Fig. 3.30, such a material is
called a direct band-gap material. For example, GaAs and InP are direct band-gap materials. For indirect
band-gap materials, the conduction band minimum and valence band maximum occur at different values of
momentum, as shown in Fig. 3.31. Silicon and germanium are indirect band-gap semiconductors.
E Electron
Hole
Conduction band
E 1
2 2
E g + ħ k 1 /m eff,1
E g
k
2 2
‒ħ k 2 /m eff,2
E 2
Valence band
Figure 3.30 Simplified E–k diagram for a direct band-gap material.