Page 136 - Fiber Optic Communications Fund
P. 136
Lasers 117
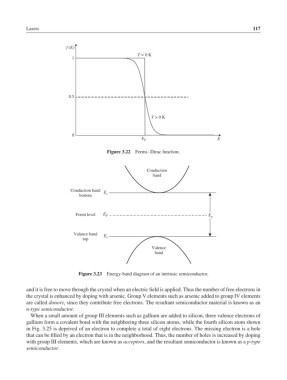
f (E)
T = 0 K
1
0.5
T > 0 K
0
E F E
Figure 3.22 Fermi–Dirac function.
Conduction
band
Conduction band E
bottom c
Fermi level E F E g
Valance band E
top v
Valence
band
Figure 3.23 Energy-band diagram of an intrinsic semiconductor.
and it is free to move through the crystal when an electric field is applied. Thus the number of free electrons in
the crystal is enhanced by doping with arsenic. Group V elements such as arsenic added to group IV elements
are called donors, since they contribute free electrons. The resultant semiconductor material is known as an
n-type semiconductor.
When a small amount of group III elements such as gallium are added to silicon, three valence electrons of
gallium form a covalent bond with the neighboring three silicon atoms, while the fourth silicon atom shown
in Fig. 3.25 is deprived of an electron to complete a total of eight electrons. The missing electron is a hole
that can be filled by an electron that is in the neighborhood. Thus, the number of holes is increased by doping
with group III elements, which are known as acceptors, and the resultant semiconductor is known as a p-type
semiconductor.