Page 324 - Fiber Optic Communications Fund
P. 324
Transmission System Design 305
10 0
w/o preamp.
10 –5
with preamp.
BER 10 –10 10 –9
10 –15
10 –20
120 140 160 180 200 220
Fiber length (km)
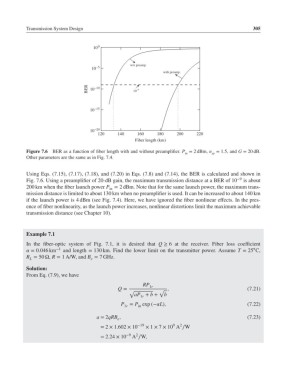
Figure 7.6 BER as a function of fiber length with and without preamplifier. P = 2dBm, n = 1.5, and G = 20 dB.
in sp
Other parameters are the same as in Fig. 7.4.
Using Eqs. (7.15), (7.17), (7.18), and (7.20) in Eqs. (7.8) and (7.14), the BER is calculated and shown in
Fig. 7.6. Using a preamplifier of 20-dB gain, the maximum transmission distance at a BER of 10 −9 is about
200 km when the fiber launch power P = 2 dBm. Note that for the same launch power, the maximum trans-
in
mission distance is limited to about 130 km when no preamplifier is used. It can be increased to about 140 km
if the launch power is 4 dBm (see Fig. 7.4). Here, we have ignored the fiber nonlinear effects. In the pres-
ence of fiber nonlinearity, as the launch power increases, nonlinear distortions limit the maximum achievable
transmission distance (see Chapter 10).
Example 7.1
In the fiber-optic system of Fig. 7.1, it is desired that Q ≥ 6 at the receiver. Fiber loss coefficient
∘
= 0.046 km −1 and length = 130 km. Find the lower limit on the transmitter power. Assume T = 25 C,
R = 50 Ω, R = 1 A/W, and B = 7 GHz.
L e
Solution:
From Eq. (7.9), we have
RP 1r
Q = √ , (7.21)
√
aP + b + b
1r
P = P exp (−L), (7.22)
in
1r
a = 2qRB , (7.23)
e
2
9
= 2 × 1.602 × 10 −19 × 1 × 7 × 10 A ∕W
2
= 2.24 × 10 −9 A ∕W,