Page 16 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 16
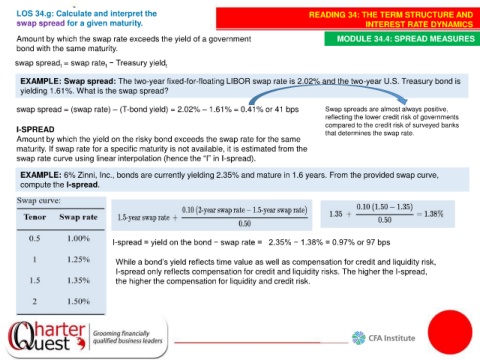
LOS 34.g: Calculate and interpret the READING 34: THE TERM STRUCTURE AND
swap spread for a given maturity. INTEREST RATE DYNAMICS
Amount by which the swap rate exceeds the yield of a government MODULE 34.4: SPREAD MEASURES
bond with the same maturity.
swap spread = swap rate − Treasury yield t
t
t
EXAMPLE: Swap spread: The two-year fixed-for-floating LIBOR swap rate is 2.02% and the two-year U.S. Treasury bond is
yielding 1.61%. What is the swap spread?
swap spread = (swap rate) – (T-bond yield) = 2.02% – 1.61% = 0.41% or 41 bps Swap spreads are almost always positive,
reflecting the lower credit risk of governments
compared to the credit risk of surveyed banks
I-SPREAD that determines the swap rate.
Amount by which the yield on the risky bond exceeds the swap rate for the same
maturity. If swap rate for a specific maturity is not available, it is estimated from the
swap rate curve using linear interpolation (hence the “I” in I-spread).
EXAMPLE: 6% Zinni, Inc., bonds are currently yielding 2.35% and mature in 1.6 years. From the provided swap curve,
compute the I-spread.
I-spread = yield on the bond − swap rate = 2.35% − 1.38% = 0.97% or 97 bps
While a bond’s yield reflects time value as well as compensation for credit and liquidity risk,
I-spread only reflects compensation for credit and liquidity risks. The higher the I-spread,
the higher the compensation for liquidity and credit risk.